RDBMS Adapter
An RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured format using rows and columns. It follows the principles of the relational model.
RDBMS databases are widely used for applications requiring reliable data storage, structured access, and robust querying capabilities. Common database systems include MSSQL, Databricks, and MySQL.
SBE Adapter/Plugin Documentation Template
Adapter & Extension Package Documentation go together
Plugins are Separate
1. Getting Started: Using the Adapter
1.1 Operations Overview
The RDBMS Adapter is a server-based SBE adapter. This allows users to interact with data from RDBMS within the Digital Thread by using the standard Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) libraries. JDBC enables the adapter to connect to relational databases, execute SQL queries, and retrieve structured data for integration into model-based engineering workflows.
Tables, rows, will be supported, currently the primary RDBMS applications supported will be Databricks and MSSQL.
Views, join tables, and advanced SQL concepts are not yet supported and may be implemented pending customer requirements.
Additional JDBC drivers and flavors of RDBMS systems (i.e.
MySQL,Oracle…) are not supported at this time.
The RDBMS Adapter expects the source SQL database to be setup with the following conditions:
All tables, to be used with the SBE, must have the following columns:
surrogateKeyas primary key & identity(defined in datasource properties)itemKey INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY
surrogateKey_clone, an empty string columnitemKey_clone VARCHAR(255)The adapter will update the _clone value from the
surrogateKeycolumn from thesurrogateKey.
namecolumnname VARCHAR(255)The column containing the name of the shape, for now this column is expected to be in all Shape tables.
Table with expected columns for Control Index
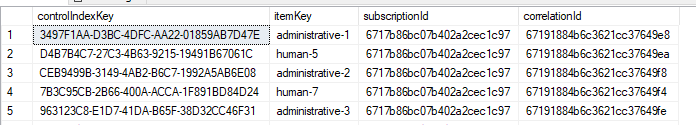
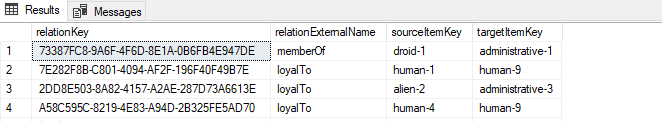
Table with expected columns for Link Table
Publish
Publish establishes a connection to a designated RDBMS host, where it retrieves all rows from the
schema.tableassociated with the channel. These rows are transformed into SBE Models.The classes are identified using the name of the table. Relations are managed by the
LinkTable, an SBE required configuration. The adapter will read this table and create links ofrelationExternalNamebetweensourceItemKeyandtargetItemKey. Columns of primitive datatypes will be converted into properties.
Refresh
Refresh establishes a connection to a designated RDBMS host, converts all models from SBE into tabular, relational data.
The classes are identified using the name of the shape ID. The adapter will not create or manage any schema or tables. There must be a table that matches each of the mapped shape IDs.
Any mapped properties will be written to to this table if there is a corresponding column.
The adapter will output model links of
relationExternalNamebetweensourceItemKeyandtargetItemKeyto theLinkTable. Columns of primitive datatypes will be converted into properties.
1.4 Publishing Items
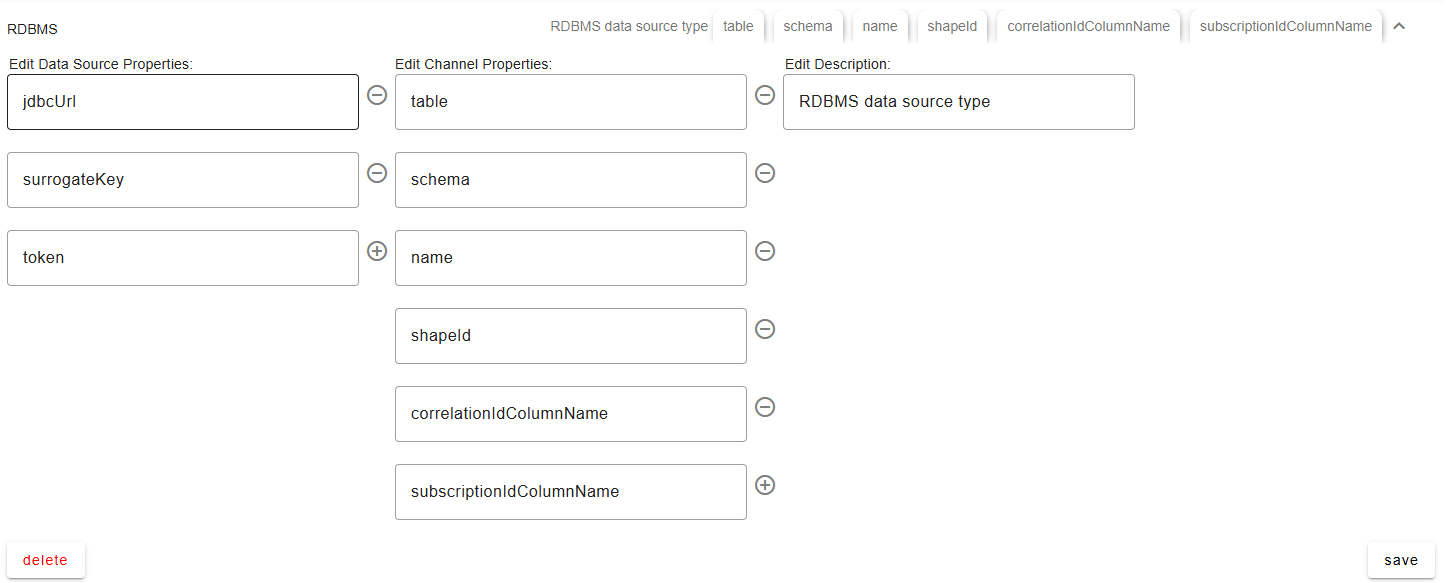
Configure an empty datasource type with the following datasource properties – using DST name: “RDBMS”
Datasource Properties
jdbcUrlJDBC url for the sql database to attach to, include the port and jdbc
ex.
jdbc:databricks://xxx.12.azuredatabricks.net:443
Include the
databaseNamefor MSSQL.ex.
jdbc:sqlserver://rdbms-mssql.com:1433;encrypt=true;trustServerCertificate=true;databaseName=e2e
tokenIf using token authentication, provide the token.
ex.
dapi4a0c9e00e30313c58xx
surrogateKeyname of the surrogateKey / primary key column for shape tables.
Default value is
itemKeyThe adapter will copy the value from this column into of the same name using suffix
_clone, i.esurrogateKey_cloneThe adapter will use this value to create objects in the control index.
Channel Properties
tabletables to retrieve data from
schemaschema to retrieve data from
nameName of column designating how a row is unique, generally a primary key or name.
correlationColumnNameName of the column in the
ControlIndextable containing the SBE correlation ID.default column is
correlationIdIf provided, the adapter uses these values to update the corresponding items in SBE.
subscriptionColumnNameName of the column in the
ControlIndextable containing the SBE subscription ID.default column is
subscriptionIdIf provided, the adapter uses these values to update the corresponding subscriptions in SBE.
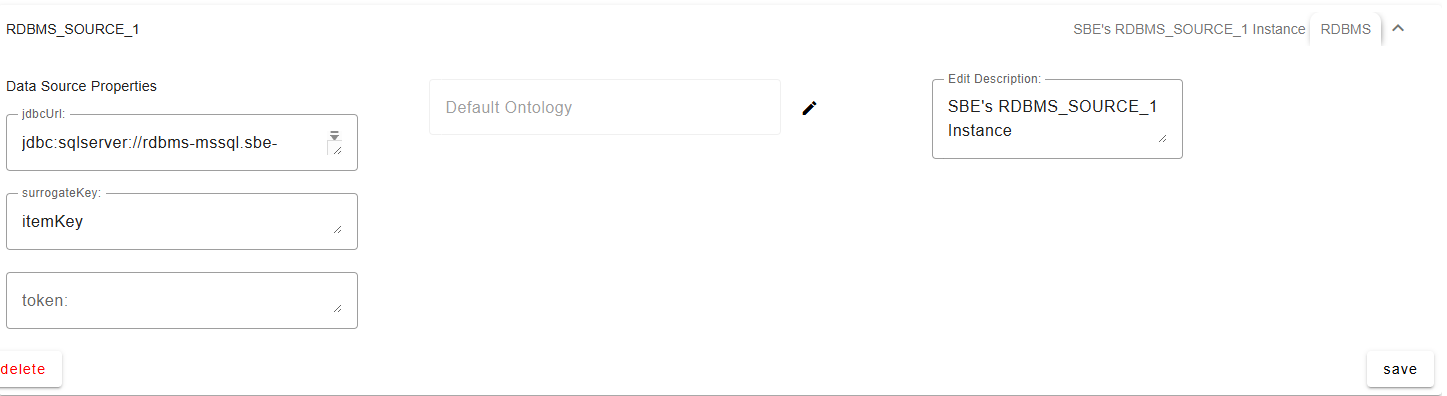
Configure an empty datasource – using any datasource name of your choosing: ex: “RDBMS_SOURCE_1”
Create a new channel partition
Optionally provide the
schema, which supports a single schema value of all the associatedtablesin the channel, by default the schema is set todboOptionally provide the
namewhich indicates thenamecolumn of the shape in the table. This will be used to determine the name of the SBE model.subscriptionColumnNamemust match a column in theControlIndextable containing the SBE subscription ID, if left empty, the adapter will attempt to usesubscriptionId.Otherwise, if not provided the the subscription ID will not be written to RDBMS.correlationIdColumnNamemust match a column in theControlIndextable containing the SBE correlation ID, if left empty, the adapter will attempt to usecorrelationId.Otherwise, if not provided the the subscription ID will not be written to RDBMS.Provide all the tables you want to use in the
tableproperty which supports a separated by any of the following delimiters:,;/|:.i.e
table1,table2,table1|table2
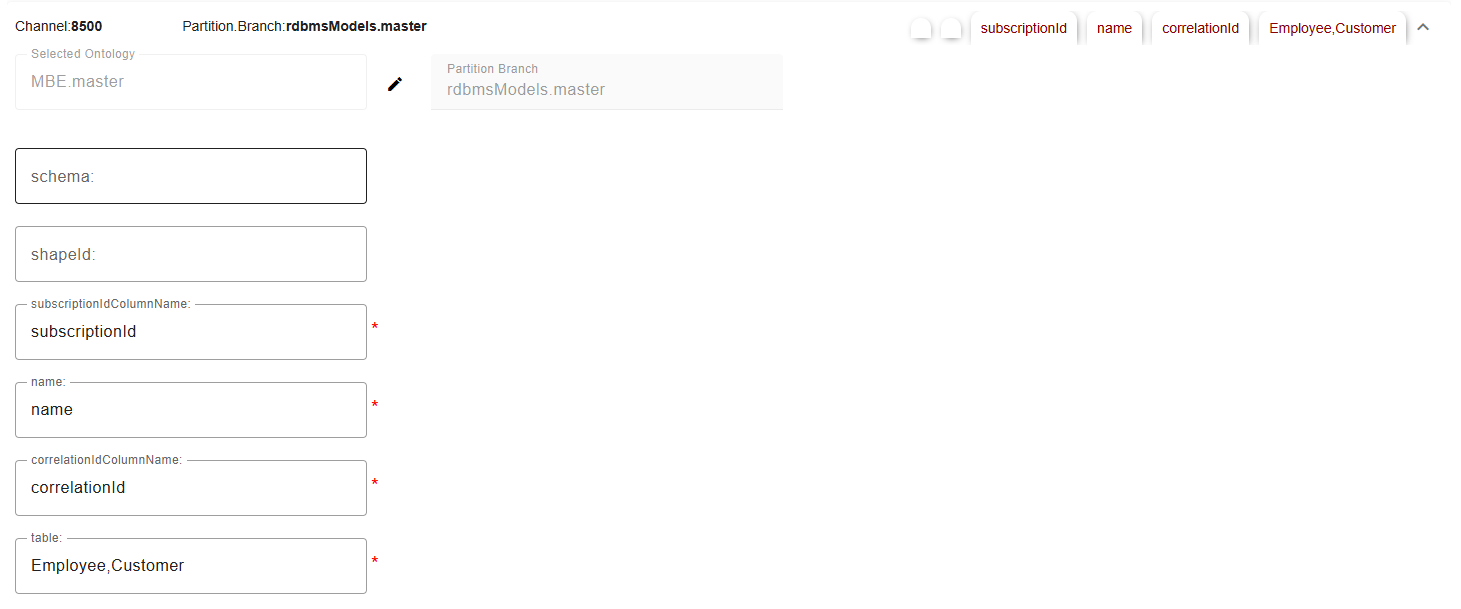
Click Publish, provide the credentials of the RDBMS server for this datasource.
1.5 Refreshing Items (Including Subscribed Items)
Configure an empty datasource type with the following datasource properties – using DST name: “RDBMS”
Datasource Properties
jdbcUrlJDBC url for the sql database to attach to, include the port and jdbc
ex.
jdbc:databricks://xxx.12.azuredatabricks.net:443
Include the
databaseNamefor MSSQL.ex.
jdbc:sqlserver://rdbms-mssql.com:1433;encrypt=true;trustServerCertificate=true;databaseName=e2e
tokenIf using token authentication, provide the token.
ex.
dapi4a0c9e00e30313c58xx
surrogateKeyname of the surrogateKey / primary key column for shape tables.
Default value is
itemKeyThe adapter will copy the value from this column into of the same name using suffix
_clone, i.esurrogateKey_cloneThe adapter will use this value to create objects in the control index.
Channel Properties
tabletables to retrieve data from
schemaschema to retrieve data from
nameName of column designating how a row is unique, generally a primary key or name.
correlationColumnNameName of the column in the
ControlIndextable containing the SBE correlation ID.default column is
correlationIdIf provided, the adapter uses these values to update the corresponding items in SBE.
subscriptionColumnNameName of the column in the
ControlIndextable containing the SBE subscription ID.default column is
subscriptionIdIf provided, the adapter uses these values to update the corresponding subscriptions in SBE.

Configure an empty datasource – using any datasource name of your choosing: ex: “RDBMS_SOURCE_1”

Create a new channel partition
Optionally provide the
schema, which supports a single schema value of all the associatedtablesin the channel, by default the schema is set todboOptionally provide the
namewhich indicates thenamecolumn of the shape in the table. This will be used to determine the name of the SBE model.subscriptionColumnNamemust match a column in theControlIndextable containing the SBE subscription ID, if left empty, the adapter will attempt to usesubscriptionId.Otherwise, if not provided the the subscription ID will not be written to RDBMS.correlationIdColumnNamemust match a column in theControlIndextable containing the SBE correlation ID, if left empty, the adapter will attempt to usecorrelationId.Otherwise, if not provided the the subscription ID will not be written to RDBMS.Provide all the tables you want to use in the
tableproperty which supports a separated by any of the following delimiters:,;/|:.i.e
table1,table2,table1|table2

Click Soft/Hard Refresh, provide the credentials of the RDBMS server for this datasource.
Supported object types/entities (overview in Section 11.3)
There is no concept of meta-classes within RDBMS systems, so we are assuming the table will be the definition of a class.
SBE Metadata and unique objects will be defined within the
ControlIndexClasses are defined by tables which are mapped to a shape ID.
Relations are supported via
LinkTable.All properties listed in the following table can be mapped to the Digital Thread.
If not listed,
Stringwill be assumed.https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/data-types/data-types-transact-sql?view=sql-server-ver17
Java Type | SQL Data Type(s) |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.6 Verify
Compares mapped database entities and subscriptions against rows in the dataset, failing if any mapped columns, metadata fields, or relations in the LinkTable do not match.
1.7 Advanced Operations
1.8 Troubleshooting for End Users
2. Document Overview
2.1 Document Overview
This document provides essential information for using, configuring, and supporting the SBE Vision adapters for RDBMS. It covers multiple adapter products, each supporting different versions of the external tool. There is a different version of this document for each major release of the SBE Platform.
2.2 Document Orientation
This document is designed to inform users with various roles:
End Users should begin with Section 1 to understand how to access and operate the adapter, and Section 5 for issues pertaining to the setup, configuration, and use of the digital tool itself.
Digital Thread Specialists should focus on Section 1, and also consult Sections 3, 4, and 5 for deployment and semantic mapping. Section 11 contains details related to mapping items from this tool into a semantic ontology.
Administrators should refer to Section 6 and beyond for setup, security, support, and version management.
3. Adapter Use Cases
3.1 Adapter Overview
The purpose of this adapter is to allow the data contained within instances of RDBMS to connect with the SBE Digital Thread platform. Given that RDBMS is a rich-client tool, the usage of this adapter is governed by end users operating that tool on the desktop of their workstation. This adapter was built using the SBE Java Pro-SDK product.
3.2 Typical Use Cases
In a Digital Thread ecosystem, RDBMS systems are essential for managing structured, relational data across the product lifecycle.
They support use cases such as configuration management, requirement traceability, bill of materials (BOM) tracking, and change management. RDBMSs enable consistent storage and querying of metadata, part catalogs, test results, and simulation data, ensuring traceability and compliance with regulatory standards.
They also serve as integration points between tools like PLM, ERP, and MES, facilitating data consistency and decision-making across domains. Additionally, RDBMSs support audit logging, security enforcement, and the generation of compliance reports, making them a foundational component in implementing and sustaining a robust Digital Thread.
Use Case 1 (Publish): Customer has existing tabular data in an relation database, such as MSSQL or Databricks. they’d like to bring that data into the Digital Thread for later use cases such as subscription to another SBE supported application (i.e. Genesys, Cameo, MATLAB, DNG).
Use Case 2 (Refresh): Customer has data from an application in the Digital Thread ecosystem that has been published to the Digital Thread, they would like to utilize this data in their relational database. The data can then be analyzed via PowerBI to produce powerful insights.
4. Supported Versions
4.1 Supported Adapter Products
7.x, 8.x, 9.x
4.2 External Tool Versions Supported
There are many flavors of SQL based RDBMS database software and services. SBE has tested MSSQL Server, Oracle DB, and Databricks, any other type of RDBMS database will have to be validated but may work with the RDBMS adapter.
SBE Verified Tool Versions
MSSQL
SQL Server 2022
Databricks
Runtime 16.4 LTS (Long-Term Support)
Oracle Database
23ai
4.3 Differences Across Tool Versions
Oracle Database uses capitalization for column and table names by default, the schema is also the name of the user. This requires all channel properties and mappings to be capitalized when using Oracle Database specifically.
4.4 Supported Plug-Ins and Add-Ons
5. Digital Tool Best Practices
5.1 Tool Configuration Considerations
The RDBMS Adapter expects the source SQL database to be setup with the following conditions:
All tables, to be used with the SBE, must have the following columns:
surrogateKeyas primary key & identity(defined in datasource properties)itemKey INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEYsurrogateKey_clone, an empty string columnitemKey_clone VARCHAR(255)The adapter will update the _clone value from the
surrogateKeycolumn from thesurrogateKey.
namecolumnname VARCHAR(255)The column containing the name of the shape, for now this column is expected to be in all Shape tables. Here is an example query for creating a block table which can be mapped to Model Blocks in SBE.
CREATE TABLE block (
itemKey INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
itemKey_clone VARCHAR(255),
name VARCHAR(255),
weight INT,
);Table with expected columns for ControlIndex
CREATE TABLE ControlIndex (
controlIndexKey UNIQUEIDENTIFIER DEFAULT NEWID() PRIMARY KEY,
itemKey VARCHAR(255),
subscriptionId VARCHAR(24),
correlationId VARCHAR(24)
);
Table with expected columns for LinkTable
CREATE TABLE LinkTable (
relationKey UNIQUEIDENTIFIER DEFAULT NEWID() PRIMARY KEY,
relationExternalName VARCHAR(255),
sourceItemKey VARCHAR(255),
targetItemKey VARCHAR(255),
);
5.2 Usage Tips & Gotchas
Common user mistakes
Recommended practices
5.3 Tool Limitations and Workarounds
Known tool-side issues
SBE-recommended solutions
6. Installation
6.1 Installation Instructions
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/database-engine/install-windows/install-sql-server?view=sql-server-ver16 https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/sql-server/sql-server-downloads
Optionally, use dedicated servers or cloud VMs (e.g., Microsoft Azure, AWS EC2, GCP Compute Engine).
Server Requirements
Component | Recommended Specification |
|---|---|
Processor (CPU) |
|
Memory (RAM) |
|
Storage |
|
Disk Space |
|
Operating System |
|
6.2 Configuration
Add the Client with client id “rdbms-adapter” to keycloak
6.3 DataSource Type Definition
Datasource Properties
jdbcUrlJDBC url for the sql database to attach to, include the port and jdbc
ex.
jdbc:databricks://xxx.12.azuredatabricks.net:443
Include the
databaseNamefor MSSQL.ex.
jdbc:sqlserver://rdbms-mssql.com:1433;encrypt=true;trustServerCertificate=true;databaseName=e2e
tokenIf using token authentication, provide the token.
ex.
dapi4a0c9e00e30313c58xx
surrogateKeyname of the surrogateKey / primary key column for shape tables.
Default value is
itemKeyThe adapter will copy the value from this column into of the same name using suffix
_clone, i.esurrogateKey_cloneThe adapter will use this value to create objects in the control index.
Channel Properties
tabletables to retrieve data from
schemaschema to retrieve data from
nameName of column designating how a row is unique, generally a primary key or name.
correlationColumnNameName of the column in the
ControlIndextable containing the SBE correlation ID.default column is
correlationIdIf provided, the adapter uses these values to update the corresponding items in SBE.
subscriptionColumnNameName of the column in the
ControlIndextable containing the SBE subscription ID.default column is
subscriptionIdIf provided, the adapter uses these values to update the corresponding subscriptions in SBE.

7. Channels and Mappings
7.1 Channel Definition
Channel Properties
project_id: (Optional) Provide the project id containing the TestRail items you want to utilize on the Digital Thread, this is typically an integer i.e.
“1”,“2”,“3”. If noproject_idis provided the adapter will publish all test cases on the testrail server.suite_id: (Optional), Project ID must not be empty if provided. If
suite_idis provided, the adapter will publish Test Cases of specified project and suite.include_test_result (Optional) When set to
“true”, includes Runs, associated Tests, and Test Results.
7.2 Approaches to Mapping
The RDBMS adapter is expecting a structure where each table is a shape and columns may become mapped as shape properties.
Any relation can be mapped as long as the schema for the
LinkTableis structured as expected.
8. Security and Access
8.1 Authentication Methods
See RFC 006 - Authentication & Authorization for the standard on how to authenticate to use SBE and adapter services.
For REST API Endpoints
Supply credentials to token end point, receive an Auth token to invoke Publish, Refresh
For SBE Platform Services
Login to SBE Platform
Currently the adapter only supports SQL Server Authentication and basic auth for Databricks.
Method | Description |
|---|---|
Windows Authentication | Uses Active Directory (AD) credentials; most secure in domain environments. |
SQL Server Authentication | Uses local logins ( |
Azure Active Directory (AAD) | For Azure SQL or SQL Server on Azure VMs; supports AAD users, groups, and MFA. |
Certificate-Based Authentication | Possible through custom integration, often for encrypted communication. |
Kerberos | AD-based single sign-on (SSO); used in enterprise environments. |
8.2 Authorization and Roles
Authentication Methods:
Built-in Authentication: Standard username/password login.
SSO (Single Sign-On): Enterprise versions may support SSO via SAML or other identity providers.
8.3 Secure Communication
All communication between clients (browsers, API consumers) and the SQL server/Databricks should be over HTTPS.
Authentication tokens are supported by JDBC connection.
8.4 Identity Integration
The adapter doesn't support these authentication methods at the time of writing but potentially may be implemented based on customer requirements. Currently only basic auth is supported for MSSQL systems and token based authentication for Databricks.
Aspect | SQL Server | Databricks |
|---|---|---|
Primary Identity Providers |
|
|
Authentication Protocols |
|
|
User Management |
|
|
Single Sign-On (SSO) |
|
|
Federation & Hybrid |
|
|
Authorization Models |
|
|
9. Troubleshooting
9.1 Logs and Diagnostics
SBE RDBMS Pod
i.e.
rdbms-adapter-5b8998d6df-6w9lc23
SQL Server
Log Type | Location / Access Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
SQL Server Error Log |
| Server startup/shutdown, critical errors, warnings |
SQL Server Agent Log |
| Job execution history and errors |
Windows Event Logs |
| System-level errors, SQL Server service events |
Trace Logs |
| Detailed query and performance tracing |
Audit Logs |
| Security-related events (logins, permission changes) |
Setup Logs |
| Installation and update activities |
Databricks
Log Type | Location / Access Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Driver and Executor Logs |
| Spark application logs, stdout, stderr |
Event Logs |
| Job and task events, status |
Audit Logs |
| Track workspace activity, user access, and changes |
Cluster Logs |
| Cluster start/stop, configuration, and failures |
Job Logs |
| Logs related to scheduled jobs and runs |
Driver Logs for SQL Analytics |
| Query execution and diagnostic logs |
10. Release Notes
10.1 Version History
8.8
V7 Item Support, store/use Ownership during ref/publish.
Fix connection leak bug while querying for metadata8.7
Upgrade SDK to 8.178.6
Update sdk to 8.15, fixes for delta pub/ref8.5
Update sdk 8.148.4
Add integration tests, support for reset service8.3
Update 8.11 sdk version, parent pom8.2
Update SDK to 8.98.1
Upgrade SDK Version 8.87.14
Fixed an issue where refresh was not updating the control index table.7.13
Updates to refresh, prevent duplicate links and items from being created and improve diff/merge7.12
Update sdk version to 7.447.11
Upgrade sdk 7.437.10
Clean up deprecated code, Support mssql, upgrade sdk7.9
Update version to 7.397.8
Update sdk version to 7.367.7
Fix Trust Store7.6
Update SDK Version to 7.337.5
Add support for verify7.4
Stateless subscription management, refresh updates source system, and rebase functionality11. Technical Reference
11.1 Adapter API Endpoints
There are no native REST API Endpoints in SQL Server.
11.2 Identity
Currently only basic auth is supported for MSSQL systems and token based authentication for Databricks.
11.3 Configuration File Format Reference
The RDBMS Adapter expects the source SQL database to be setup with the following conditions:
All tables, to be used with the SBE, must have the following columns:
surrogateKeyas primary key & identity(defined in datasource properties)itemKey INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEYsurrogateKey_clone, an empty string columnitemKey_clone VARCHAR(255)The adapter will update the _clone value from the
surrogateKeycolumn from thesurrogateKey.
namecolumnname VARCHAR(255)The column containing the name of the shape, for now this column is expected to be in all Shape tables. Here is an example query for creating a block table which can be mapped to Model Blocks in SBE.
CREATE TABLE block (
itemKey INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
itemKey_clone VARCHAR(255),
name VARCHAR(255),
weight INT,
);Table with expected columns for ControlIndex
CREATE TABLE ControlIndex (
controlIndexKey UNIQUEIDENTIFIER DEFAULT NEWID() PRIMARY KEY,
itemKey VARCHAR(255),
subscriptionId VARCHAR(24),
correlationId VARCHAR(24)
);
Table with expected columns for LinkTable
CREATE TABLE LinkTable (
relationKey UNIQUEIDENTIFIER DEFAULT NEWID() PRIMARY KEY,
relationExternalName VARCHAR(255),
sourceItemKey VARCHAR(255),
targetItemKey VARCHAR(255),
);
11.4 Schema Support
Supported object types/entities (overview in Section 11.3)
There is no concept of meta-classes within RDBMS systems, so we are assuming the table will be the definition of a class.
SBE Metadata and unique objects will be defined within the
ControlIndexClasses are defined by tables which are mapped to a shape ID.
Relations are supported via
LinkTable.All properties listed in the following table can be mapped to the Digital Thread.
If not listed,
Stringwill be assumed.https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/data-types/data-types-transact-sql?view=sql-server-ver17
Java Type | SQL Data Type(s) |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Directionality: bi-directional
11.5 Glossary of Terms
Common technical terms across tools/adapters
11.6 Compliance and Certification
ITAR, DoD, or cybersecurity compliance info (if applicable)
Adapter Maturity Model ratings
