OSLC3 Consumer
1. Getting Started: Using the Adapter
1.1 Operations Overview
Oslc3-consumer is a server-based SBE adapter. This allows users to interact with data from DNG within the Digital Thread via the DNG OSLC API.
Publish
Publishing moves data from DNG to the Digital Thread.
During publish, oslc3-consumer fetches the artifacts from the DNG server as OSLC RDF data. This RDF data is then mapped by the SBE SDK to item DTOs using the rdf:resource types as the shape ids, before being sent to the SBE platform, where the items are published as SBE models on the Digital Thread using the ontology mappings.
Refresh
Refreshing moves data from the Digital Thread to DNG.
During refresh, the SBE platform maps the models to item DTOs, which are sent to oslc3-consumer. The oslc3-consumer then maps the item DTOs to OSLC RDF format and posts them to the DNG server.
Verify
Verifying compares the data between the Digital Thread and DNG. Results, viewable in the “Detailed” Tracking Logs, show an item-by-item comparison of each corresponding DNG artifact/SBE model pair, indicating any discrepancies between the two in properties, relations, or metadata.
Reset
The Reset operation checks the Digital Thread for stale (deleted) subscriptions and removes the corresponding, previously subscribed, items from the attached DNG project/stream.
1.2 Accessing the Adapter
Since oslc3-consumer is a server-based adapter, the connection between DNG and the Digital Thread is managed by SBE, and all operations are performed via the SBE web interface. Once the connection is established, as described in Section 1.3, all data operations described above can be initiated and monitored within the SBE platform.
1.3 Attaching & Connecting
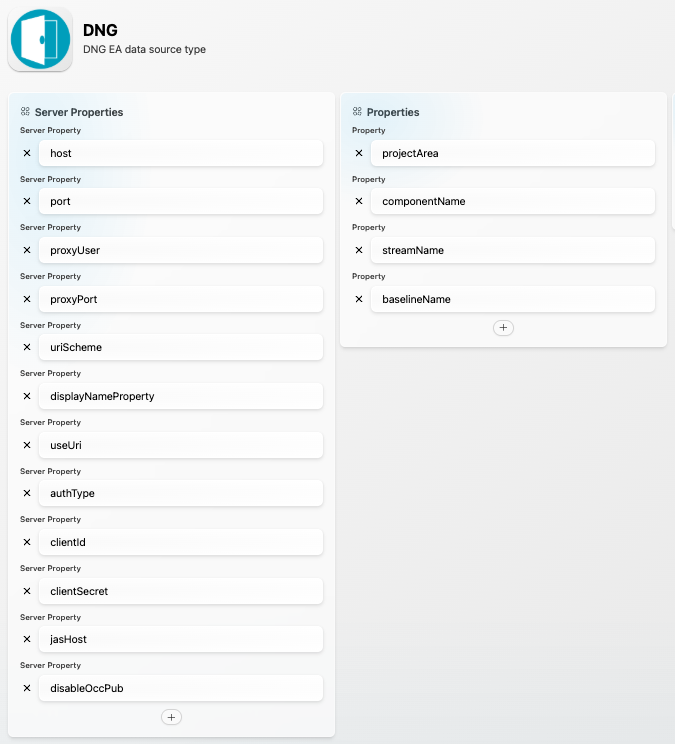
The following properties must be configured via the SBE Data Source Manager:
Data Source Type: DNG
Data Source Properties:
Name | Description | Required? |
|---|---|---|
host | Host name of DNG | Yes |
port | Port at which DNG runs | No |
uriScheme | Http or https | Yes |
proxyUser | Proxy user can be empty | No |
proxyPort | Proxy port at which DNG can run, this can be empty | No |
displayNameProperty | Property used as display name property on items. Valid values are: | No |
authType | Authentication type on ELM. Valid values are: | No |
clientId | Used only for | No |
clientSecret | Used only for | No |
jasHost | Jazz Authorization Server hostname (if different from DNG hostname) | No |
disableOccPub | If set to | No
|
Channel properties:
Name | Description | Required? |
|---|---|---|
projectArea | Project Area | Yes |
componentName | Component Name | Yes |
streamName | Stream Name | Yes |
baselineName | Baseline Name | No |
Example DST config:
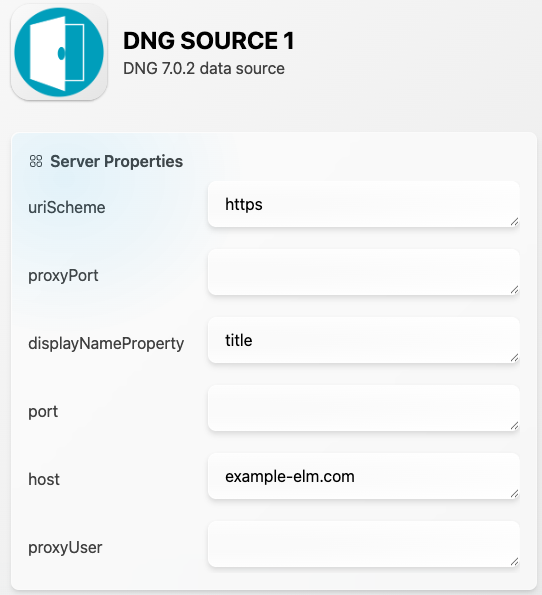
Example DS config:
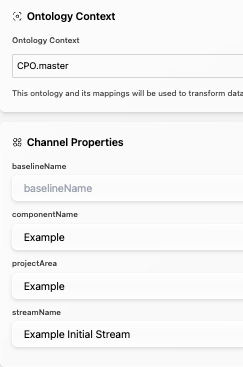
Example Channel config:
1.4 Publishing Items
Publishes can be triggered from the SBE UI:
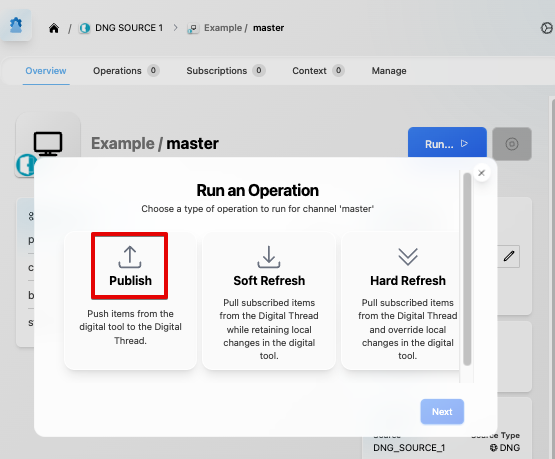
Oslc3-consumer supports publishing the following domains: requirements, folders, modules/occurrences, and collections.
DNG has a concept of module occurrences which is not an oslc concept; module occurrences are pointers to DNG artifacts that are contained by a module:
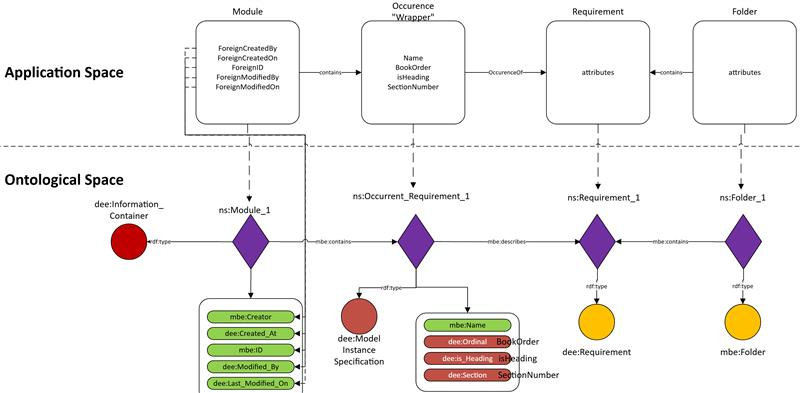
As of oslc3-consumer release 7.14, we can toggle the publishing of module occurrences such that modules have containment links directly to the requirement artifacts, rather than pointing to occurrences, which then point to requirements. By default, module occurrences are published. To disable the publishing of module occurrences, set the datasource property disableOccPub = true:

1.5 Refreshing Items (Including Subscribed Items)
Refreshes can be triggered from the SBE UI:
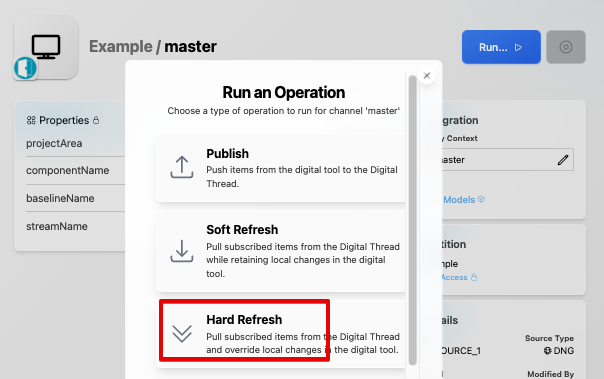
Hard refresh overwrites any changes in DNG since the last publish with changes from the Digital Thread. Soft refresh (aka rebase) does NOT overwrite changes in DNG since the last publish; only items in DNG that have NOT been updated since the last publish will be updated by rebase.
Oslc3-consumer supports refreshing creates, updates, and deletes of requirements. For folders, modules/occurrences, and collections, oslc3-consumer only supports refreshing deletes. Consequently, oslc3-consumer only supports subscribing to requirements from other data sources.
In order to support subscriptions to requirements from other data sources, two artifact attribute types must be added to DNG’s component properties: DigitalThreadSubscriptionId and DigitalThreadCorrelationId:
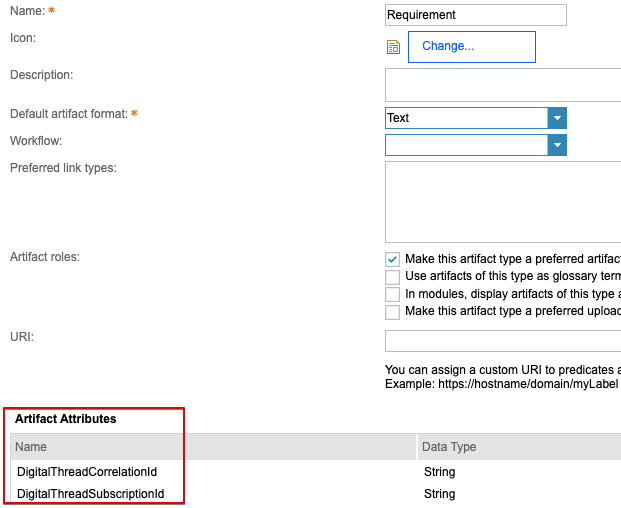
These attributes are populated and utilized by oslc3-consumer:
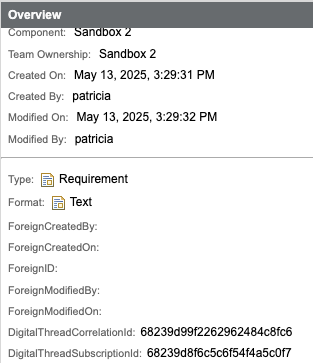
Subscribed requirements will appear in subfolders labeled by ASOT partition and entity set, under a parent Digital Thread folder:
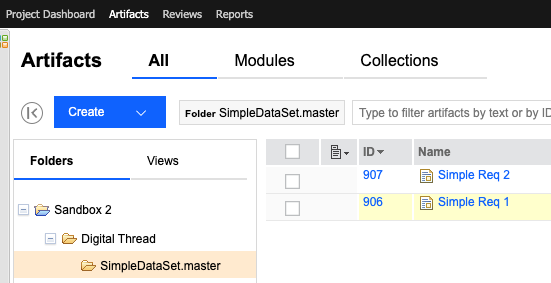
These folders are merely organizational. They are NOT published/refreshed/managed by the Digital Thread. Furthermore, moving the artifacts out of the relevant Digital Thread folder will NOT unsubscribe the artifacts or make them ASOT (i.e. authoritative).
1.6 Verify
As described in Section 1.1, the verify operation compares the data between the Digital Thread and DNG. It can be triggered from the SBE UI:
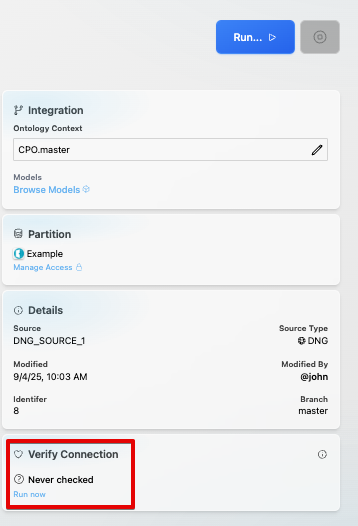
1.7 Advanced Operations
Reset
As described in Section 1.1, reset deletes stale subscribed items out of DNG. It is currently supported by the oslc3-consumer, and can be initiated by clicking the Reset button from the SBE UI:
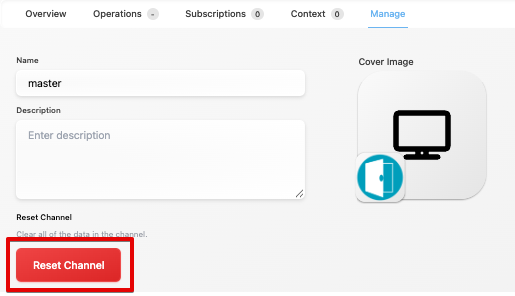
1.8 Troubleshooting for End Users
Most issues arise from misconfigurations of DNG. See Sections 5.2 and 6.2 below for help troubleshooting configurations.
If data is wiped from a stack, but subscribed items remain in DNG, then subsequent publishes may fail and/or be corrupted. In this case, the reset operation must be triggered to delete all stale subscribed items from DNG.
1.9 Upgrade steps for SBE platform 6.x->7.x
For wakefield (6.x) → woburn (7.x) migrations, upgrade must be triggered for all channels for all adapters. For improved usability, multi-channel upgrades have been implemented for oslc3-consumer. Multi-channel upgrades can be triggered via the same api as standard upgrades (i.e. /x/relays/connectors). Multi-channel upgrades will upgrade each channel one at a time in numerical order. The payloads are as follows:
Single-channel upgrade (standard):
{
"channel": "1",
"subject": "refresh",
"intent": "upgrade",
"waypoint": "browser",
"info": {
"username": "{{DNG_username}}",
"password": "{{DNG_password}}",
"authType": "ldap"
}
}Multi-channel upgrade (will upgrade channels 1 and 2):
{
"channel": "1",
"subject": "refresh",
"intent": "upgrade",
"waypoint": "browser",
"hints": {
"upgrade-option": "upgrade-many",
"upgrade-channels": "1,2"
},
"info": {
"username": "{{DNG_username}}",
"password": "{{DNG_password}}",
"authType": "ldap"
}
}All-channel upgrade (will upgrade all channels for the Data Source associated with the provided channel):
{
"channel": "1",
"subject": "refresh",
"intent": "upgrade",
"waypoint": "browser",
"hints": {
"upgrade-option": "upgrade-all"
},
"info": {
"username": "{{DNG_username}}",
"password": "{{DNG_password}}",
"authType": "ldap"
}
}2. Document Overview
2.1 Document Overview
Oslc3-consumer is a server adapter that supports SBE operations for external tools that implement OSLC (Open Services for Lifecycle Collaboration) standards for data sharing. These standards specify the interactions between lifecycle tools across varying domains, including change, test, requirement, and configuration management, with the goal of seamless integration and interoperability between these tools. At its core, OSLC dictates the representation of resources in RDF format and the linking between resources using URIs.
Currently, the tool that is supported by oslc3-consumer is DNG (DOORS Next Generation), which implements OSLC for data sharing with other tools. DNG is a requirements management tool within the IBM Engineering Lifecycle Management (ELM) suite, a set of tools built on the IBM Jazz platform. The main features of DNG include: creation/import/export of requirement artifacts; hierarchical organization of artifacts; linking between artifacts; tracing of links; version control; auditing; and collaboration. These artifacts can take on a variety of data formats, such as text, tables, images, etc., though the oslc3-consumer supports the following data types: string, boolean, integer, float, enum. Per OSLC, these artifacts are published out of DNG in RDF format (which the oslc3-consumer consumes as XML), which contains metadata and URIs pointing to the resources in DNG, thus allowing for the discovery and modification of said resources through HTTP requests.
This document provides essential information for using, configuring, and supporting the SBE Vision adapters for DNG. It covers multiple adapter products, each supporting different versions of the external tool. There is a different version of this document for each major release of the SBE Platform.
2.2 Document Orientation
This document is designed to inform users with various roles:
End Users should begin with Section 1 to understand how to access and operate the adapter, and Section 5 for issues pertaining to the setup, configuration, and use of the digital tool itself.
Digital Thread Specialists should focus on Section 1, and also consult Sections 3, 4, and 5 for deployment and semantic mapping. Section 11 contains details related to mapping items from this tool into a semantic ontology.
Administrators should refer to Section 6 and beyond for setup, security, support, and version management.
3. Adapter Use Cases
3.1 Adapter Overview
The purpose of this adapter is to allow the data contained within instances of DNG to connect with the SBE Digital Thread platform. Given that DNG is a server-side tool, all SBE operations are performed via the SBE web interface. This adapter was built using the SBE Java Pro-SDK product.
4. Supported Versions
4.1 Supported Adapter Products
8.x (features that are specific to a version are noted throughout this document)
4.2 External Tool Versions Supported
DNG 6.0.6 and DNG 7.0.2 - DNG 7.1.0 are supported by oslc3-consumer
4.3 Differences Across Tool Versions
There are no major functional differences between DNG 6.x and DNG 7.x; the most significant changes are under-the-hood changes, such as to the underlying data store (see here and here) and to the Jazz Authorization Server (see here). For other changes, please consult the DNG 7.x release notes.
4.4 Supported Plug-Ins and Add-Ons
DNG provides a client extension API to develop JavaScript plugins. There is currently no DNG plugin developed by SBE.
5. Digital Tool Best Practices
5.1 Tool Configuration Considerations
Please follow the instructions in Section 6.2 carefully, as slight deviations from the correct configurations may result in failures to publish / refresh via oslc3-consumer.
5.2 Usage Tips & Gotchas
Ensure that licenses and roles have been properly assigned to end users; otherwise, SBE operations may fail with 403s (See Section 6.2)
Configuration Management must be enabled for proper functioning of oslc3-consumer (See Section 6.2)
The DigitalThreadSubscriptionId and DigitalThreadCorrelationId artifact attributes must be added to any project for which subscription is desired (See Section 1.5)
If you are not seeing certain artifacts and/or links as expected on the Digital Thread, ensure that the Artifact and Link types are properly configured in the “Manage Component Settings” section of your DNG project, and make sure that these types match the ontology mappings being used for DNG / oslc3-consumer.
5.3 Tool Limitations and Workarounds
There are currently no major limitations and workarounds that we know of with respect to oslc3-consumer workflows.
6. Installation
6.1 Installation Instructions
DNG installation instructions can be found on the official IBM docs. For example, 6.0.6 here and 7.0.2 here. The installation instructions list the system requirements for a variety of supported platforms and operations systems. See also the installation instructions for Jazz Team Server and Jazz Authorization Server (if applicable).
6.2 Configuration
Enabling Configuration Management
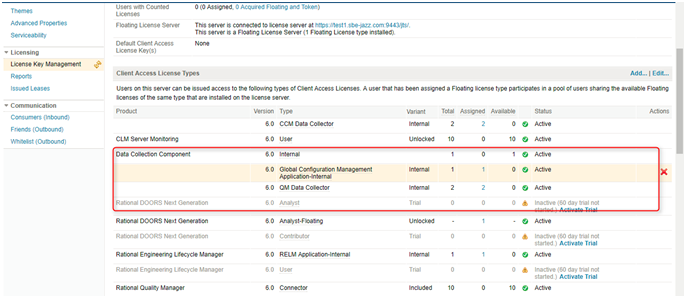
Step 1: Check if GC is installed with it in build license:
Login to Jazz Team Server (/jts/admin)
Click on Manage Server. -> Click on License key Management. -> Check that Global Configuration Management Application-Internal is “Active”
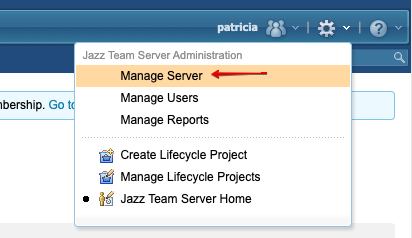
Step 2: Getting Key from Jazz.net. for enabling Configuration management for RM/ DNG.
URL : https://jazz.net/servlet/clm-cm/request-key?version=6.0.3&lang=en_US
It will ask you for Jazz credentials give credentials and generate key for desired version.
Step 3: provide details of what version you are using and respective language.
It will generate a key for you. Copy the key to some secure location.
Initially we will be enabling Configuration Management for JTS
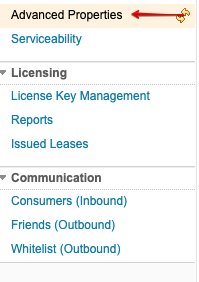
Step 4:
Navigate to Advanced Properties from jts/admin → Manage Server left sidebar
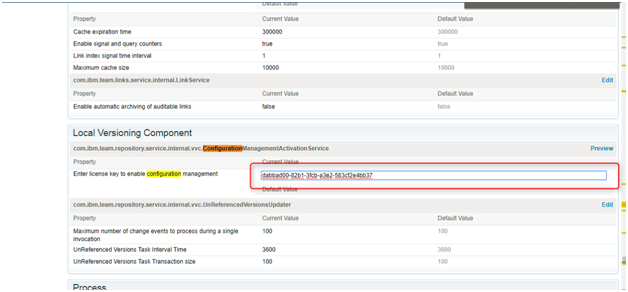
Step 5: Search for "ConfigurationManagementActivation Service" locate "Enter license key to enable configuration management" and add the generated key into it.
Note : Now we have added configuration management for JTS (Jazz Team Server), similarly we have to add it for DNG/RM. (Requirement Management)
Step 6: To enable configuration management for DNG/RM, navigate to /rm/admin left sidebar → Advanced Properties.
Step 7: Search for Configuration management and -> Click on Edit button to add generated Key.
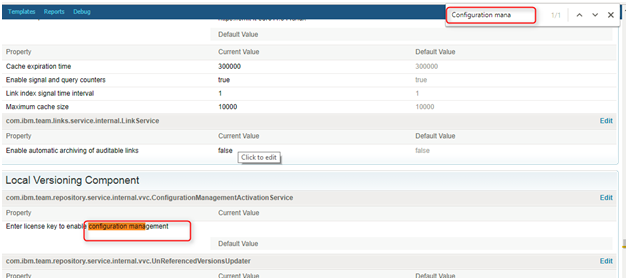
Step 8: To enable configuration management for a given project area:
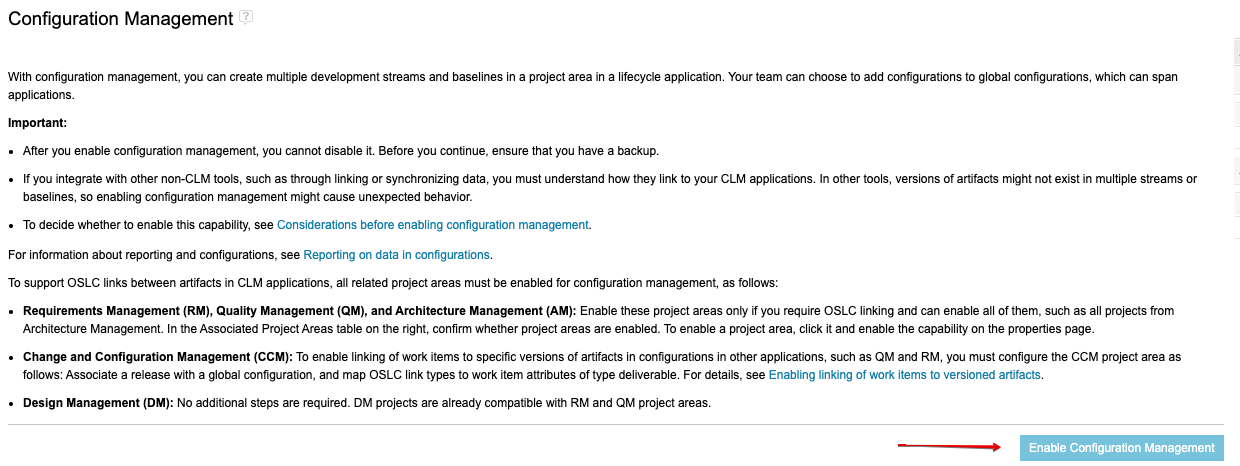
From “Manage This Project Area”, click on “Configuration Management” and click “Enable Configuration Management”
Creating Project Areas
Login to Jazz Team Server (/jts/admin)
→ ”House” drop down menu → Requirements Management → All Projects → Manage All Projects
Click “Create Project Area”
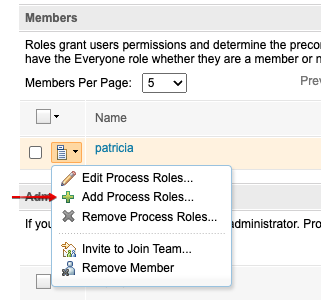
Members: search for and add users
Add all roles
You may need to add the roles manually after creating the project area and saving (see screenshot)
These roles are required for publish/refresh operations
Administrators: search for and add users
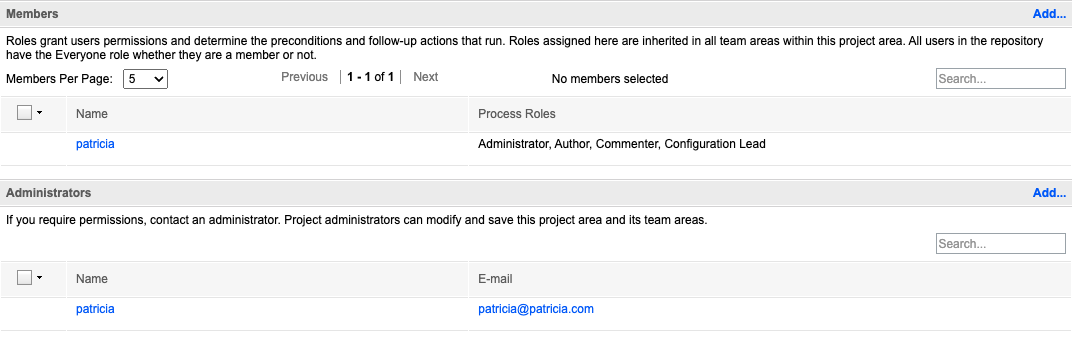
Ensure you enable configuration management (see Enabling Configuration Management - Step 8)
Linking RM project → GC project
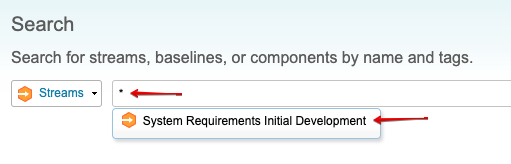
Once GC project area and RM project area are created, you can add the RM project area configuration to the GC project area as follows:
Navigate to GC project area and search for stream with *:
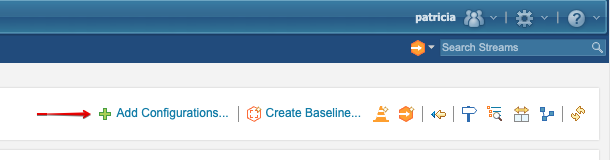
Click “Add Configurations”:
Search for RM stream by project area and component:
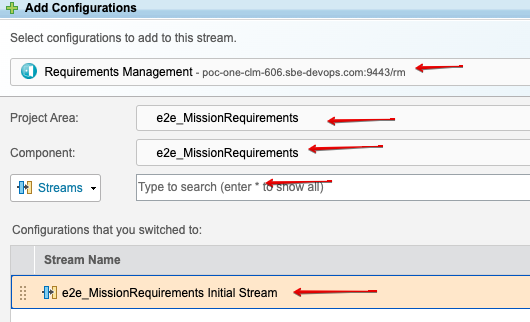
6.3 Data Source Type Definition
Data Source Type: DNG
Data Source Properties:
host: Host name of DNG (Required)
port: Port at which DNG runs (Optional)
uriScheme: http or https (Required)
proxyUser: Proxy user (Optional)
proxyPort: Proxy port at which DNG can run (Optional)
displayNameProperty: Property used as display name on items. Valid values: identifier, title (Optional)
authType: Authentication type on ELM. Valid values: oauth, basic, custom (Optional)
(See Section 8 below for more info)
clientId: Used only for custom auth type (Optional)
clientSecret: Used only for custom auth type (Optional)
jasHost: Jazz Authorization Server hostname (if different from DNG hostname) (Optional)
disableOccPub: If true, module occurrences are not published and modules link directly to requirements (Optional)
(See Section 1.5 for more info)
Example DS config:

7. Channels and Mappings
7.1 Channel Definition
projectArea: Project Area (Required)
componentName: Component Name (Required)
streamName: Stream Name (Required)
baselineName: Baseline Name (Optional)
Note: baselines can only be published, not refreshed, since baselines are frozen; thus, refreshes on baselines will be rejected
Example channel config:

7.2 Approaches to Mapping
This table lists the shapes coming out of DNG that will need to be mapped to the Digital Thread:
Shape ID | Shape Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
METACLASS | OSLC requirement spec | |
METACLASS | OSLC requirement collection spec | |
ELM_TYPE | DNG requirement collection (extends OSLC requirement collection) | |
ELM_TYPE | DNG requirement text | |
ELM_TYPE | DNG module | |
Artifact Type (e.g. Requirement) | STEREOTYPE | DNG artifact type |
Folder | METACLASS | DNG folders can contain subfolder, modules and requirements. |
ModuleOccurrence | main | DNG requirement occurrence when under a module; contains additional props with respect to module and points to requirement reference |
Example mapping for Requirements:
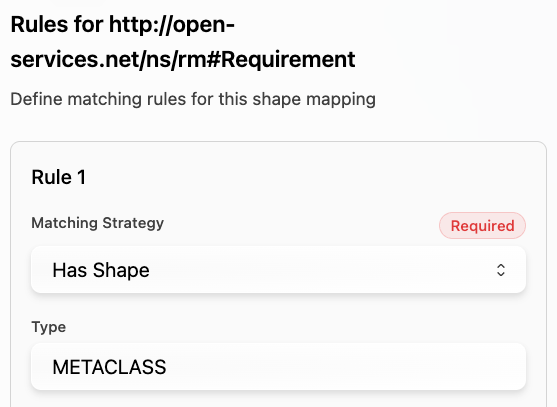
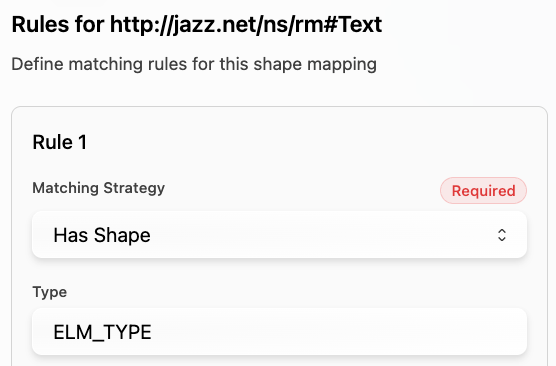
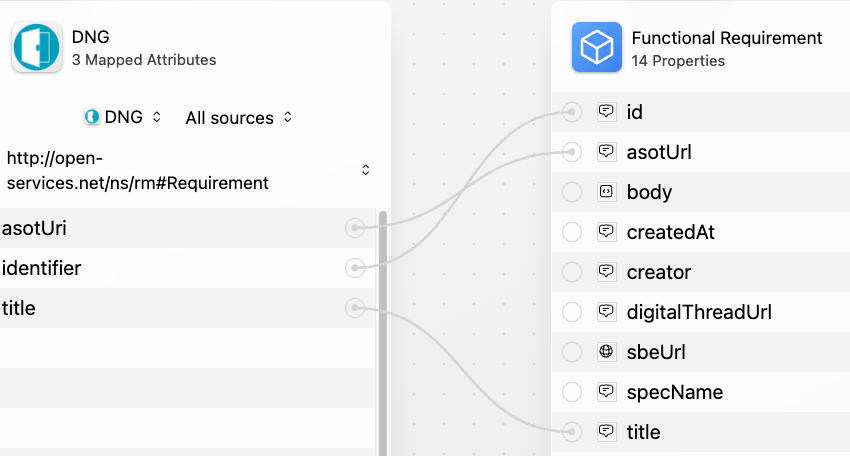
This table lists the properties and relations coming out of DNG by shape type:
Shape | Properties | Relations |
|---|---|---|
Requirement, Requirement Collection, Module |
| |
Text |
|
|
Folder |
|
|
Module Occurrence |
|
|
Example property mappings:
Example relation mappings:
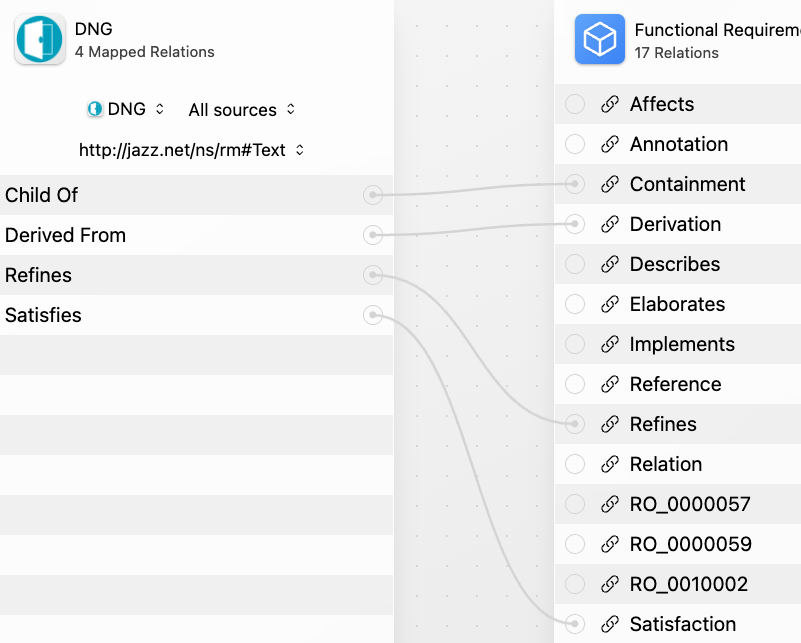
IMPORTANT: the external relation name MUST match the outgoing label of the link as defined in the component properties' link types config:
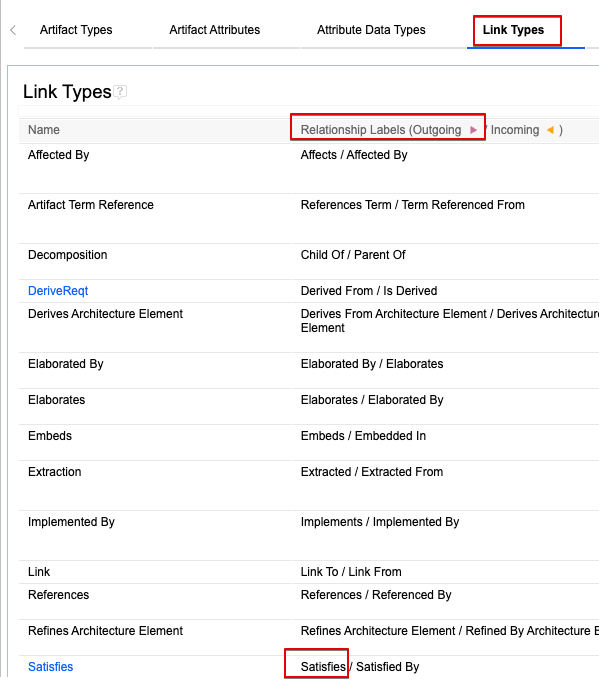
8. Security and Access
8.1 Authentication Methods
See RFC 006 - Authentication & Authorization for the standard on how to authenticate to use SBE and adapter services.
For REST API Endpoints
Supply credentials to token end point, receive an Auth token to invoke Publish, Refresh
For SBE Platform Services
Login to SBE Platform
As noted in Section 6.3 above, there are three auth types supported by oslc3-consumer: basic, oAuth, and custom.
basic: This should be used for DNG instances for which Jazz Authorization Server has NOT been set up. This is uses basic authentication against DNG with username / password credentials. If no authType data source property is specified, this is the default configuration.
oAuth: This should be used for DNG instances for which Jazz Authorization Server has been set up. This auth flow follows X-JSA-Authorization redirects from JAS, makes a basic auth request, sets session cookies, and makes subsequent requests to DNG with the authenticated session.
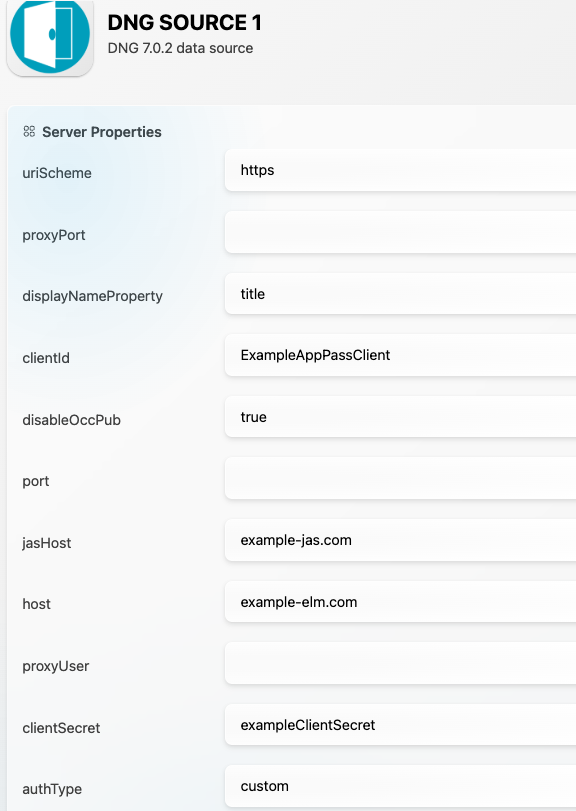
custom: This should be used for DNG instances for which Jazz Authorization Server has been set up and for which liberty application passwords are necessary. Liberty application passwords must be created for the Jazz Authorization Server following these instructions. The username should be provided via the SBE UI as well as the generated liberty application password. The clientId and the clientSecret data source properties must also be provided, which are the client id and secret for the JAS app password client (as indicated the instructions linked above). The jasHost property is optional- only needed when the Jazz Authorization Server hostname is different from the Jazz/DNG hostname.
Example DS config for custom auth type:
8.2 Authorization and Roles
In order for SBE operations to succeed, read/write roles must be properly assigned to DNG users on a per-project basis, as described in Section 6.2 - “Creating project areas”.
When DNG is set up using LDAP / Jazz Authorization Server, special care must be taken to map users to roles via Jazz Team Server role mappings to match role mappings in the LDAP server, since group mappings are not automatically synced between JTS and the LDAP in use. See this section of the IBM documentation for more information.
8.3 Secure Communication
All communication between clients (browsers, API consumers) and the DNG server should be over HTTPS.
This ensures encryption in transit, protecting:
Login credentials
API requests/responses
8.4 Identity Integration
Oslc3-consumer supports both locally managed identity management (i.e. via Jazz Team Server) and identity management through Jazz Authorization Server and LDAP, which in turn supports SAML and other third-party OIDC IdPs. The instructions on how to configure Jazz Authorization Server and Jazz Team Server to support LDAP along with third-party OIDC IdPs can be found in this section of the IBM documentation.
9. Release Notes
9.1 Version History
7.16
Fix internal event handler break statements
7.15
Support subscriptions
Implement reset
7.14
Toggle module occurrence publishing
7.13
Support JAS token / password grant auth
Fix link deletion bug
Bump SDK to 7.47
7.12
Support multi-channel upgrades
7.11
Support publishing baselines
Implement verify
Bump SDK version to 7.45
7.10
Bump SDK version
7.9
Bump SDK version
7.8
Bumped SDK version
7.7
Support async, multi-threaded operations and Spring event-based handling
Fix ReadinessService to handle incorrect server URL/props and credentials
Align with more up-to-date adapter design
7.6
SDK 7.33
7.5
Bug fix – relation creation
7.4
SDK 7.27
Renamed relation from ContainedIn to ContainedInFolder
Relation delete
7.3
Upgrade (Woburn) one channel at a time
SDK 7.20
7.2
Support uri as property names using DS properties
Readiness validation on channel
Support item delete
7.1
Support rebase
7.0
Added adapter readiness
Deprecated ResourceDTO
Support refresh
Support upgrade
Use intents
SDK storage
New project versioning
8.3
Bump SDK to 8.9 and fix link deletion
8.2
Implement verify
Support baseline publishing
Bump SDK to 8.8
8.1
Support multi-threaded processing of SBE operations
8.0
Support SBE 8.0
9.2 Breaking Changes
(6-7) There is an update available to avoid using URIs as external item identifiers such that in the event of a DNG server migration, the models / links on the digital thread wouldn’t be wiped out by changes to the external item identifiers. However, this requires a managed migration rollout.
(7 → 8) There are currently no breaking changes introduced in 8.x releases
10. Technical Reference
10.1 Adapter API Endpoints
At a high level, the main DNG interactions during SBE operations are as follows:
To get DNG project area, component, and stream info (basically called once when SBE operation is triggered):
get rootservices.xml for DNG API discovery - this exposes the chain of subsequent DNG OSLC API endpoints to be called
get service providers (i.e. project areas) for DNG instance
get project area services.xml (i.e. creation factories, query capabilities)
get components for project area
get streams for component
project area, component, and stream URIs (which correspond to the channel props) are then used to read / write DNG resources throughout the rest of SBE operation
then, for a publish:
get component properties (i.e. artifact, attribute, link types; basically called once)
get all DNG resources in batch (in oslc RDF format; called once)
each DNG resource needs to then be fetched individually (e.g. for rdf:type shape info, which is unavailable on initial batch query; number of DNG calls increases linearly with DNG artifact count)
for each DNG resource, we also fetch all outbound links
or, for a refresh
post to the relevant DNG creation factory endpoints as exposed by the project area services.xml (e.g. /rm/resources, /rm/folders, /rm/links, etc.)
The actual API endpoints are OSLC-compliant and can be discovered through the rootservices and services documents, as specified by the OSLC API.
10.2 Identity
Currently, the external locator (i.e. identifier) for all DNG artifacts are the OSLC “about” URIs (e.g. https://example-dng.com/rm/resources/TX_rN0wkAjnEfC4_ocyPaOPXg). However, as noted in Section 10.2 above, there is an update available to migrate the external locators to only use the identifier string, rather than the whole URI (e.g. TX_rN0wkAjnEfC4_ocyPaOPXg).
10.3 Configuration File Format Reference
N/A - oslc3-consumer does not use a configuration file
10.4 Schema Support
The shape ids are taken from the incoming RDF resources from DNG, which are then mapped to their corresponding shape types in oslc3-consumer as indicated in Table 1 below.
The properties and relations are also taken from the incoming RDF resources and are mapped according to OSLC requirements management specifications as indicated in Table 2 below.
Table 1: Shape Ids → Shape Types
Shape ID | Shape Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
METACLASS | OSLC requirement spec | |
METACLASS | OSLC requirement collection spec | |
ELM_TYPE | DNG requirement collection (extends OSLC requirement collection) | |
ELM_TYPE | DNG requirement text | |
ELM_TYPE | DNG module | |
Artifact Type (e.g. Requirement) | STEREOTYPE | DNG artifact type |
Folder | METACLASS | DNG folders can contain subfolder, modules and requirements. |
ModuleOccurrence | main | DNG requirement occurrence when under a module; contains additional props with respect to module and points to requirement reference (see Table 2 ModuleOccurrence properties) |
Table 2: Shapes → Properties and Relations
Shape | Properties | Relations |
|---|---|---|
Requirement, Requirement Collection, Module |
| |
Text |
|
|
Folder |
|
|
Module Occurrence |
|
|
10.5 Compliance and Certification
Maturity | Key Verification Parameters |
|---|---|
Level 1 | Design Ready, Review documentation |
Level 2 | Technology Demonstrated for initial scope. |
Level 3 | Test full-publish, full-refresh on authoritative and subscribed entity sets on current release train. Review Architecture. |
Level 4 | Test all actions on current and future release trains. Test mandatory telemetry. Basic tests are automated. Review Architecture and adoption of best practices. |
Level 5 | Tuned for performance. Introspectable. Full test automation. Stable for 6 months. |
Level 6 | Realizes all domains. Automated L3-L5 tests passes. Stable for 6 months. |
Level 7 | Ongoing security and dependency patches. Stable for a year. |
Oslc3-consumer is currently rated at Level 4 in the adapter maturity model.
