Elasticsearch Adapter
SBE Adapter/Plugin Documentation Template
Adapter & Extension Package Documentation go together
Plugins are Separate
1. Getting Started: Using the Adapter
1.1 Operations Overview
The Elasticsearch Adapter is a server-based SBE adapter, allowing the transfer of data from an Elasticsearch NoSQL database to the SBE platform and vis-versa.
Elasticsearch is a distributed search and analytics engine designed to provide near real-time search and analytics for all types of data. Regardless of its search and analytic capabilities, for our purposes, at its heart, Elasticsearch is a NoSQL database that stores object data as JSON formatted documents that can be accessed in bulk or by query.
An Elasticsearch index, simply put, is a collection of documents. Each document in an index may have the same properties (key-value pairs), or they may vary from item to item. However, all fields and their datatypes will be added to the index and available in the schema.
Elasticsearch primarily communicates via the HTTP protocol and is therefore designed to be interacted with via any web-connected system. However, the SBE Elasticsearch adapter utilizes the Elasticsearch Java API, which allows easy access to and interaction with Elasticsearch data via Java-based applications
Connect
Connecting is the process of connecting your Elasticsearch source to the digital thread. This process is performed behind the scenes by SBE when initiating one of the operations described below (publish, refresh, etc). Necessary details of your Elasticsearch project, specifically the connection string (url), and indices to be published/refreshed, are provided as server and channel properties, as described in Section 1.3.
Publish
The Publish operation moves data from a connected system into the SBE platform.
In publishing Elasticsearch data to SBE, the index name will be used as the ShapeId, unless another shapeId is specified in the “indices” Channel Property, as described in Section 1.3.
The “_source” field of the Elasticsearch doc (record) contains the item attributes (key-value pairs). These will be mapped directly to properties of the SBE model representing the doc.
SBE supports relations/links between items in the same or different indices via the “sbe_relations_index” index (Relations Index). The Relations Index entries are described in detail in section 11.4.
A Publish of Elasticsearch data can be initiated from the SBE web-UI by following the steps outlined in Section 1.4.
Hard-Refresh
The Hard-Refresh (Refresh) operation moves data from the SBE platform to a connected system.
In refreshing data into Elasticsearch from the digital thread, indices will be created for each data shape, with index name matching shapeId, unless another index name is specified for a given shapeId in the “indices” Channel Property, as described in Section 1.3.
Mapped SBE model properties will be written to the “_source” field of the Elasticsearch doc as a key-value pair (property name : value).
Each relation/link in the digital thread dataset will be represented by a single entry in the Relations Index, specifying the source item, relation name and target item, as described in Section 1.4.
An additional index, “sbe_control_index” will be automatically created and populated to store metadata for subscribed items. This data is necessary to tie subscribed records in elasticsearch back to SBE models when published back to the digital thread. Users should not modify this index.
Soft-Refresh
Like the Hard-Refresh, the Soft-Refresh operation, moves data from the digital thread to the connected system. However, in this operation, Elasticsearch records will be updated with the latest version of the corresponding SBE model unless the item has been edited in the Elasticsearch index since the most recent publish to the digital thread.
This is the equivalent of merging the data with all merge conflicts being resolved in favor of the data within the connected Elasticsearch project.
Verify
The Verify operation examines the data in the digital thread and the connected elasticsearch project to “verify” that the data is in sync. Results, viewable in the “Detailed” Tracking Logs, show an item-by-item comparison of each corresponding ES doc and its model representation in the Digital Thread, indicating any discrepancies between the two in properties, relations or metadata.
Reset
The Reset operation checks the digital thread for stale (deleted) subscriptions and removes the corresponding, previously refreshed, items from the connected Elasticsearch project.
1.2 Accessing the Adapter
The connection between Elasticsearch and the digital thread is managed by SBE and all operations are performed via the SBE web interface (Digital Thread Hub) or associated APIs. Once the connection is established, as described in Section 1.3, all data operations described above can be initiated and monitored within the SBE platform.
1.3 Connecting
Establishing a connection between your Elasticsearch project and the digital thread can be completed using the Connection Manager on the Digital Thread Hub. Once in the Connection Manager, follow the steps below to create a Source Type, Source and Channel.
Source Type
The Source Type is a generic designator that tells SBE the identity of the external system that a Data Source, Channel or Connection are targeting. The Elasticsearch adapter handles all operations on Channels tied to Elasticsearch, as indicated by an associated Source Type with name “ELASTICSEARCH”.
The ELASTICSEARCH Source Type can be associated with multiple Sources, thus allowing connection to multiple Elasticsearch projects and indices on different channels. To accommodate this, the Source Type specifies two sets of properties, Server Properties and Channel Properties.
To create an ELASTICSEARCH Source Type, click the Gear icon in the upper right of the Connection Manager UI. Select “Create Source Type”.
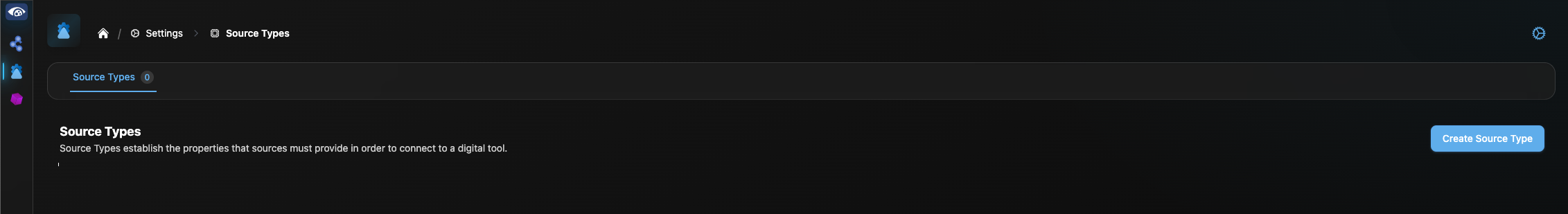
In the Configure screen, create the ELASTICSEARCH Source Type as shown below. The Source Type should have one Server Property: “connectionString” and one Channel Property: “indices”, as seen below. Click “Create Source Type” in the bottom right.
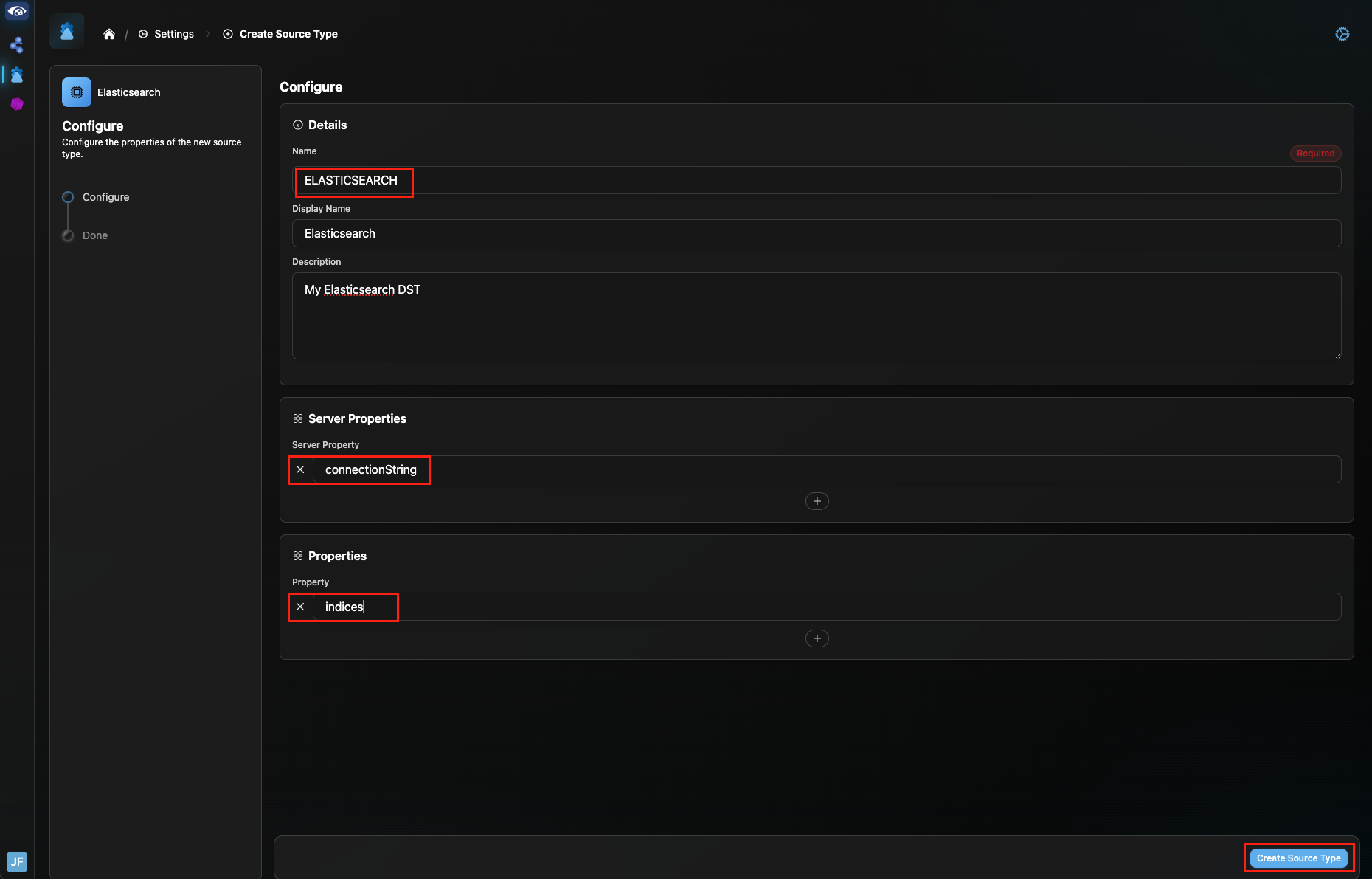
Configure the ELASTICSEARCH Data Source Type
Data Source
The Source specifies the Elasticsearch project to which the digital thread will connect. This project location (url) is specified by the connectionString Server Property, set up on the Source Type above.
You should now see the new Elasticsearch Source Type on the Source Types menu.
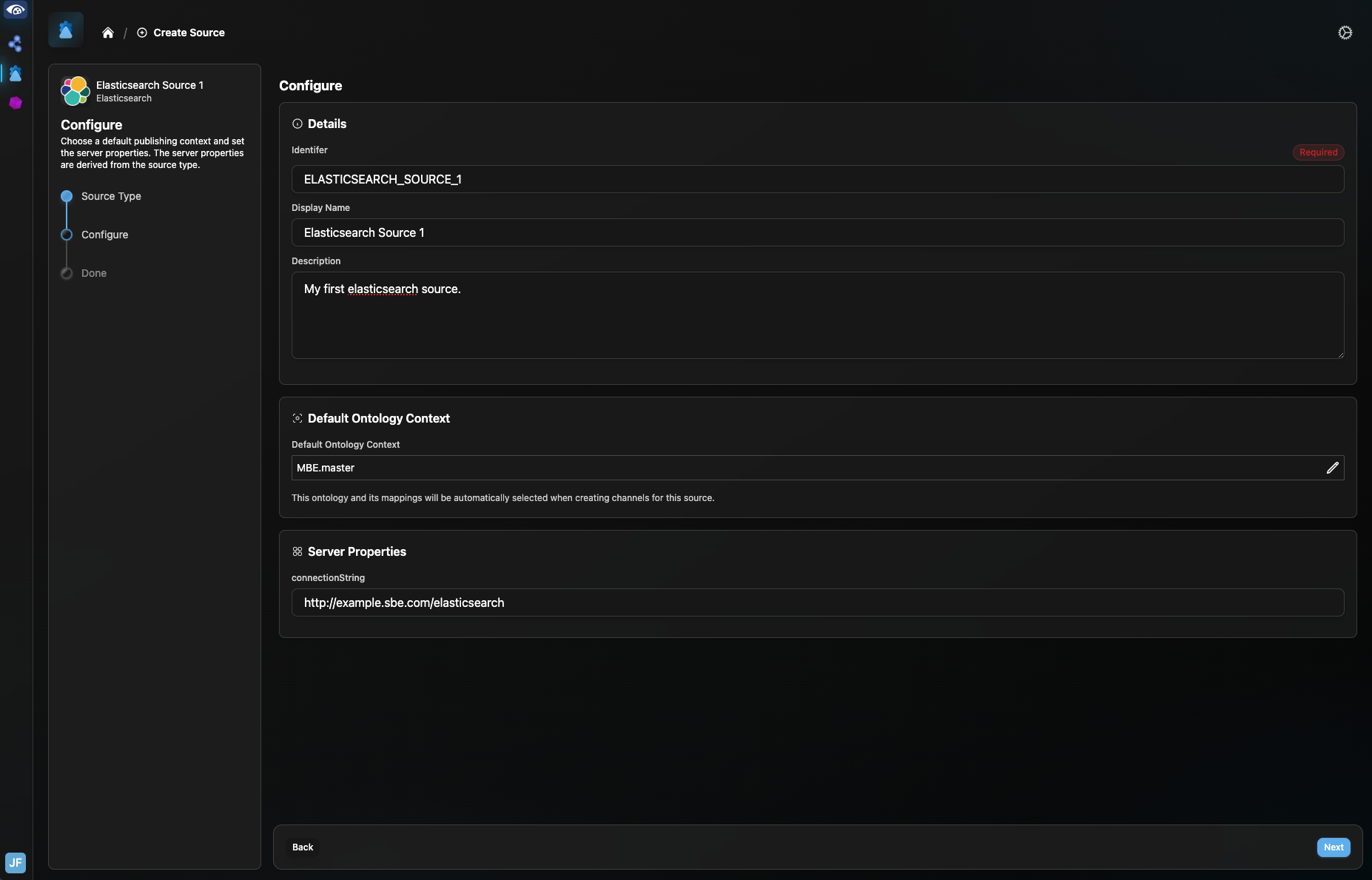
Click the Home icon to return to the Sources menu. Select “Create Source” and select the Elasticsearch Source Type. On the Source Configure page, name the Source and add a default ontology and description if desired. Enter the URL of your elasticsearch project in the “connectionString” property field, as shown below. Click “Next” in the lower right to see confirmation of creation of the Source. Click “Done” to be directed to the new Source.
Channel
The Channel details the two endpoints of data operations between your Elasticsearch project and the digital thread.
From the Connection Manager home page, select the Source that you just created and select “Channels” from the header bar.
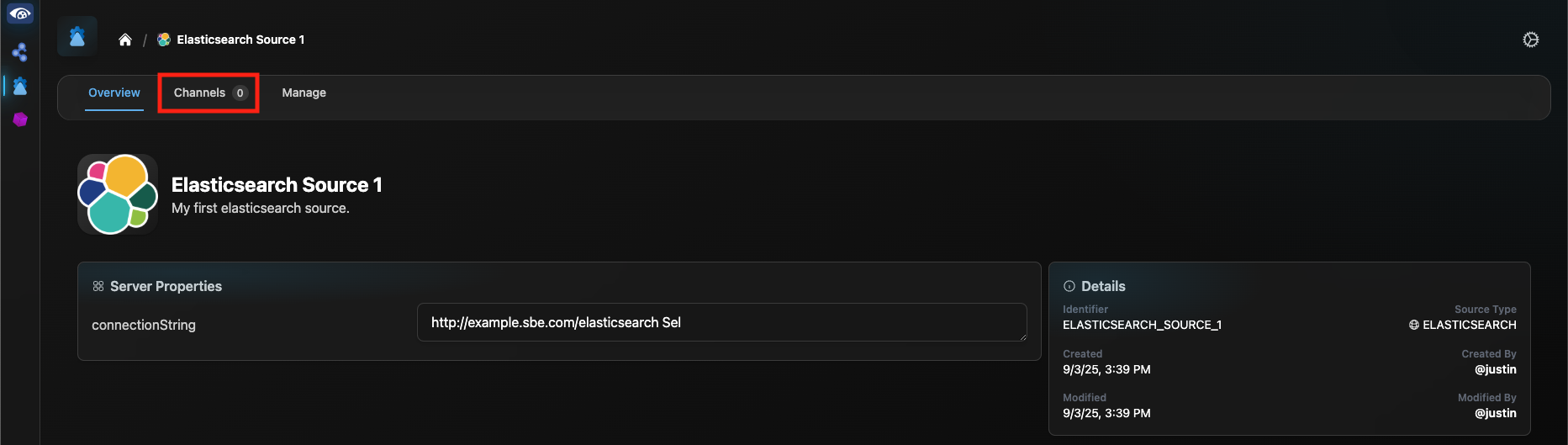
Click “Create Channel”. If a partition exists that you would like to connect to, select it from the Partition dropdown. Otherwise, select the “Create a new partition instead” checkbox, enter details for the new partition and click “Next”.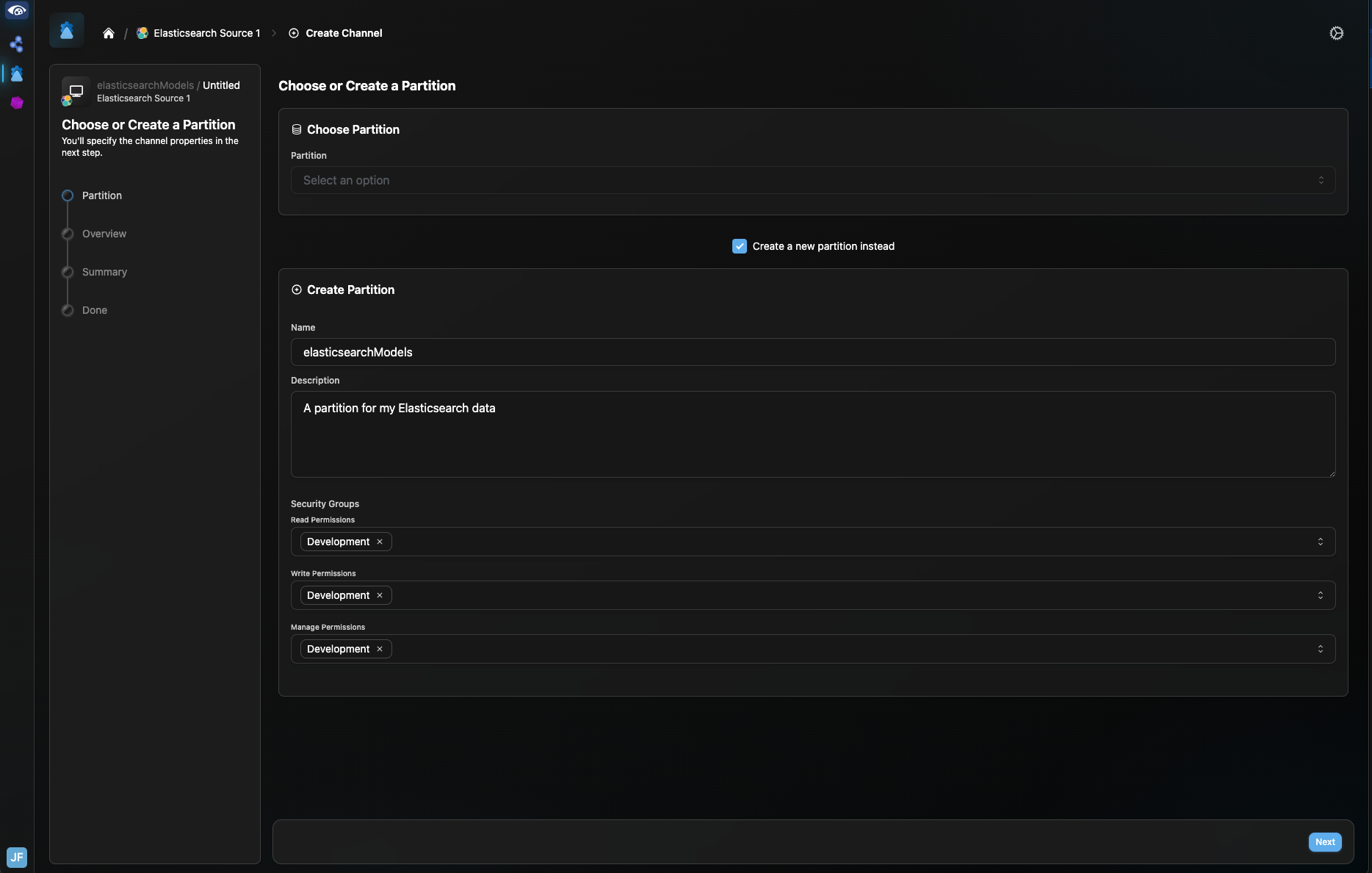
Give your channel a name and set the ontological context. Set the indices Channel Property, as described in Section 7.1 and click “Next”.
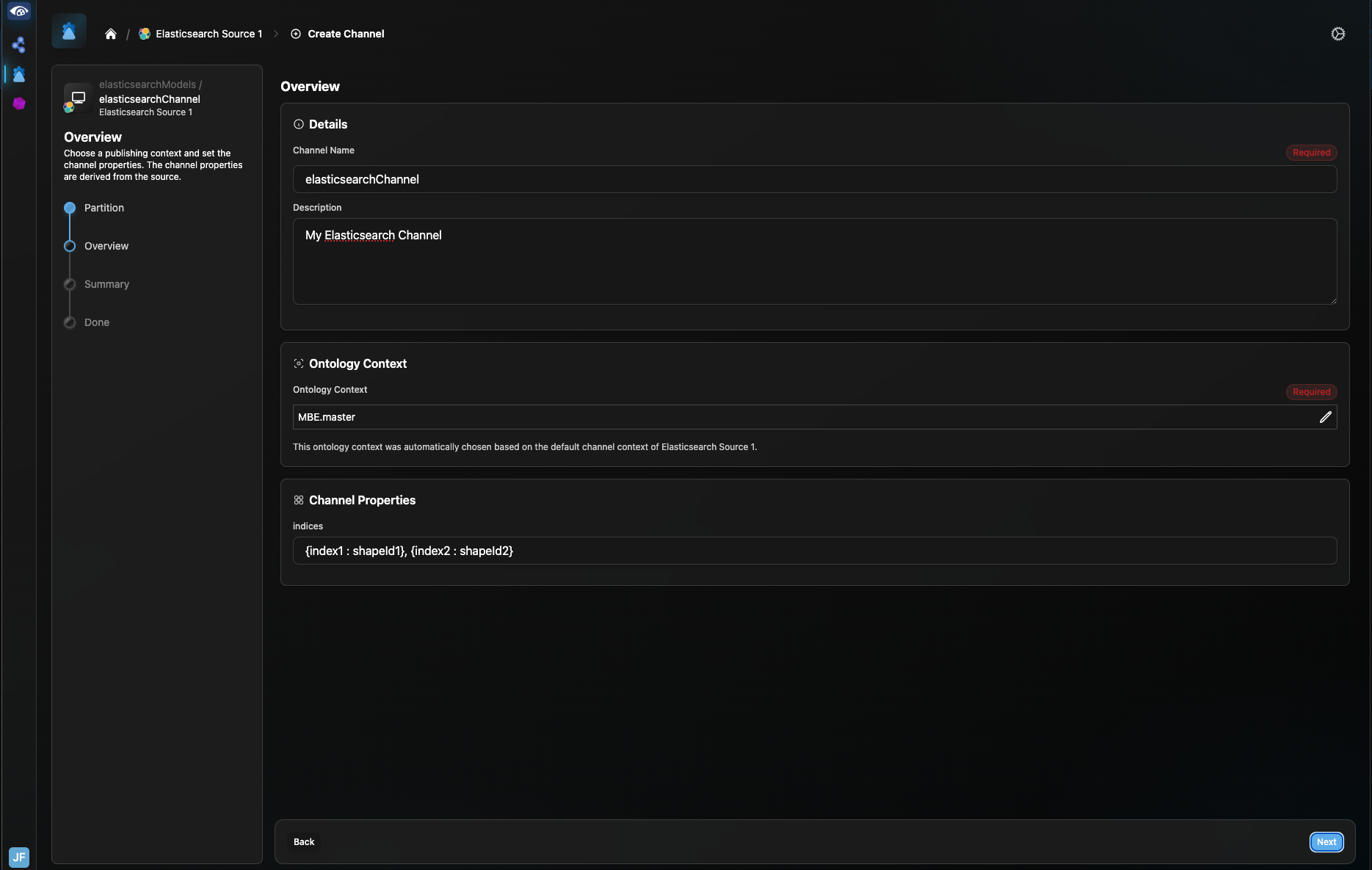
Review the channel details on the Channel Summary page and click “Create Channel”.
1.4 Publishing Items
Create a Source Type, Source and Channel as described in Section 1.3 above.
Ensure that all indices from the Elasticsearch project to be published are included in the “indices” Channel Property, along with the mapped shapeId to which they will published.
In the Connection Manager, click the link to the channel for your Elasticsearch Source. Click on the channel name to go to the Channel Overview screen. On this screen, you can review the “indices” property to ensure all indices to be published are included. Click the Run button in the upper right. Select “Publish” in the pop up and select “Next”.
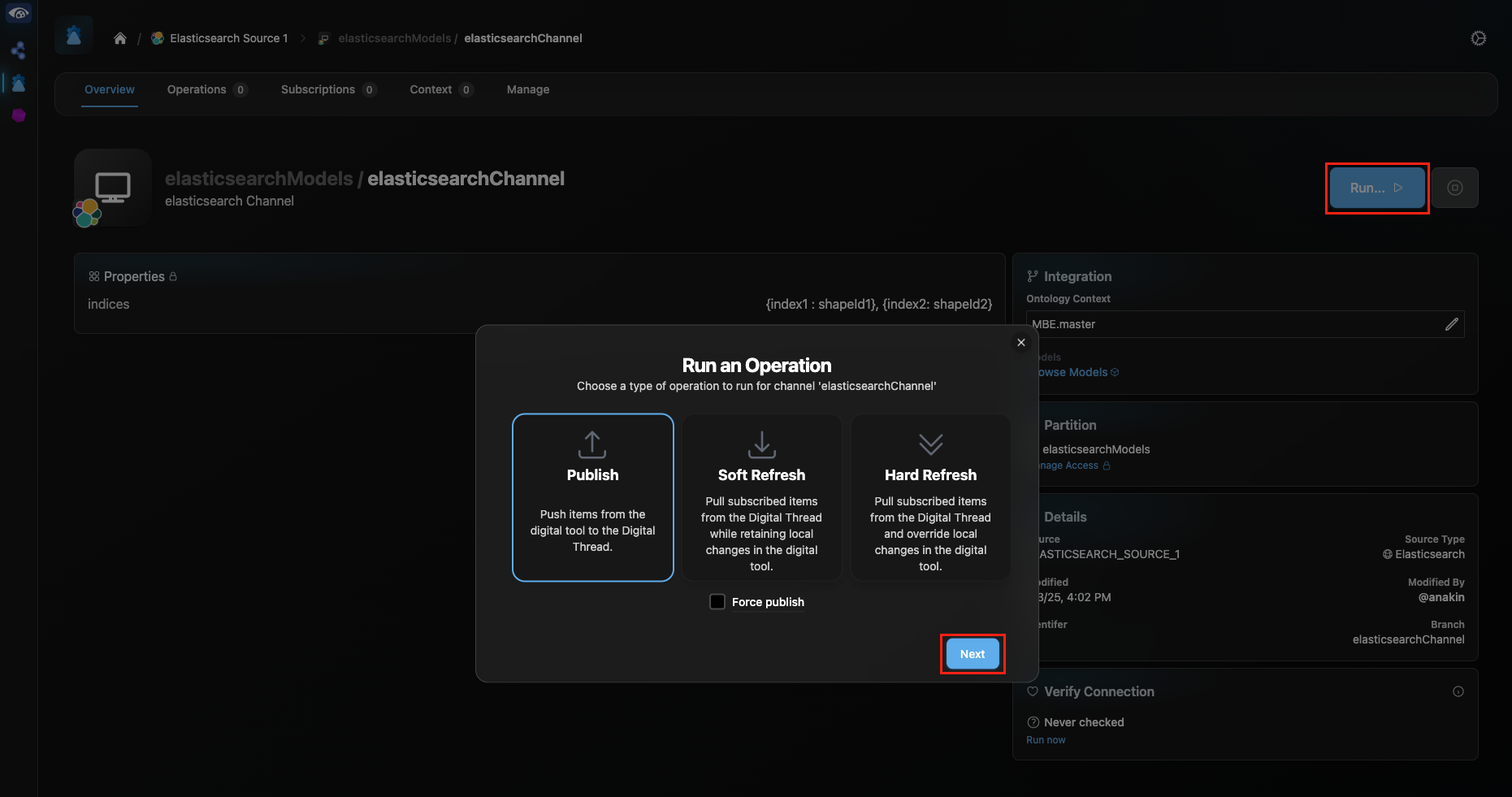
Enter your Elasticsearch credentials in the next pop-up and click “Next”. You will be redirected to the Channel Operations page, where you can track the progress of your publish.
1.5 Refreshing Items (Including Subscribed Items)
Assuming that Source Type, Source and Channel have been set up, initiating a Refresh operation, as with Publish, can be performed from the Channel Overview page for your channel in the Connection Manager.
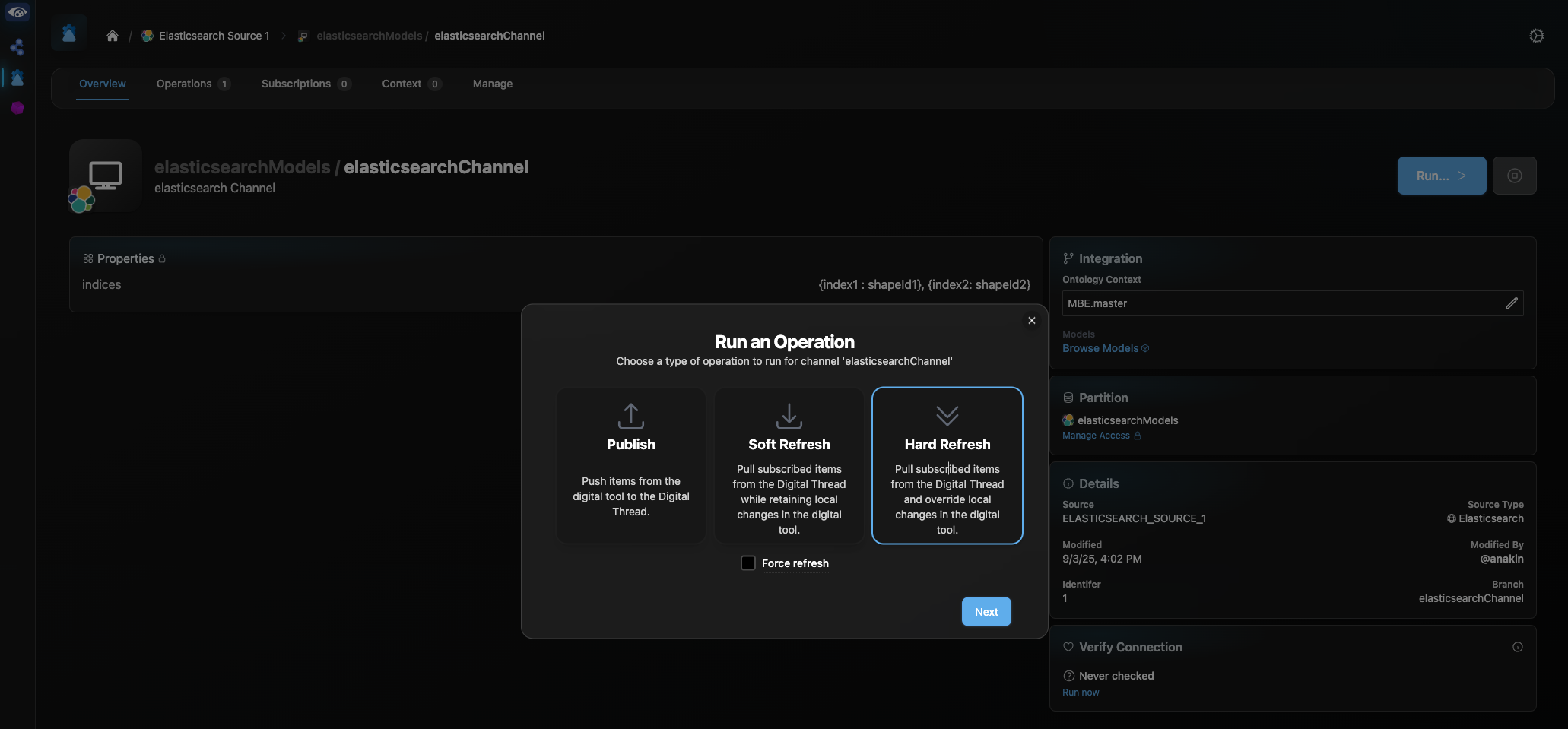
Click Run. In the pop-up, select “Hard Refresh” to refresh data from the digital thread to the connected Elasticsearch project.
Authoritative models, those originating from the Elasticsearch project via a previous Publish operation on the channel, will be updated, including any changes to properties or relations, in the same indices from which they originated. Existing docs will be overwritten with updated versions from the digital thread.
Subscribed models, those originating from projects or systems outside of the channel will be written to the indices matching their shapeIds, as specified in the “indices” Channel Property. If the index does not exist, it will be created by the adapter. If a subscribed item’s shapeId is not included in the “indices” Channel Property list, the index name will simply be the same as the shapeId. Note: index names will be adjusted as necessary to meet Elasticsearch index naming requirements.
Enter your Elasticsearch credentials in the next pop-up and click “Next”. You will be redirected to the Channel Operations page, where you can track the progress of your refresh.
1.6 Verify
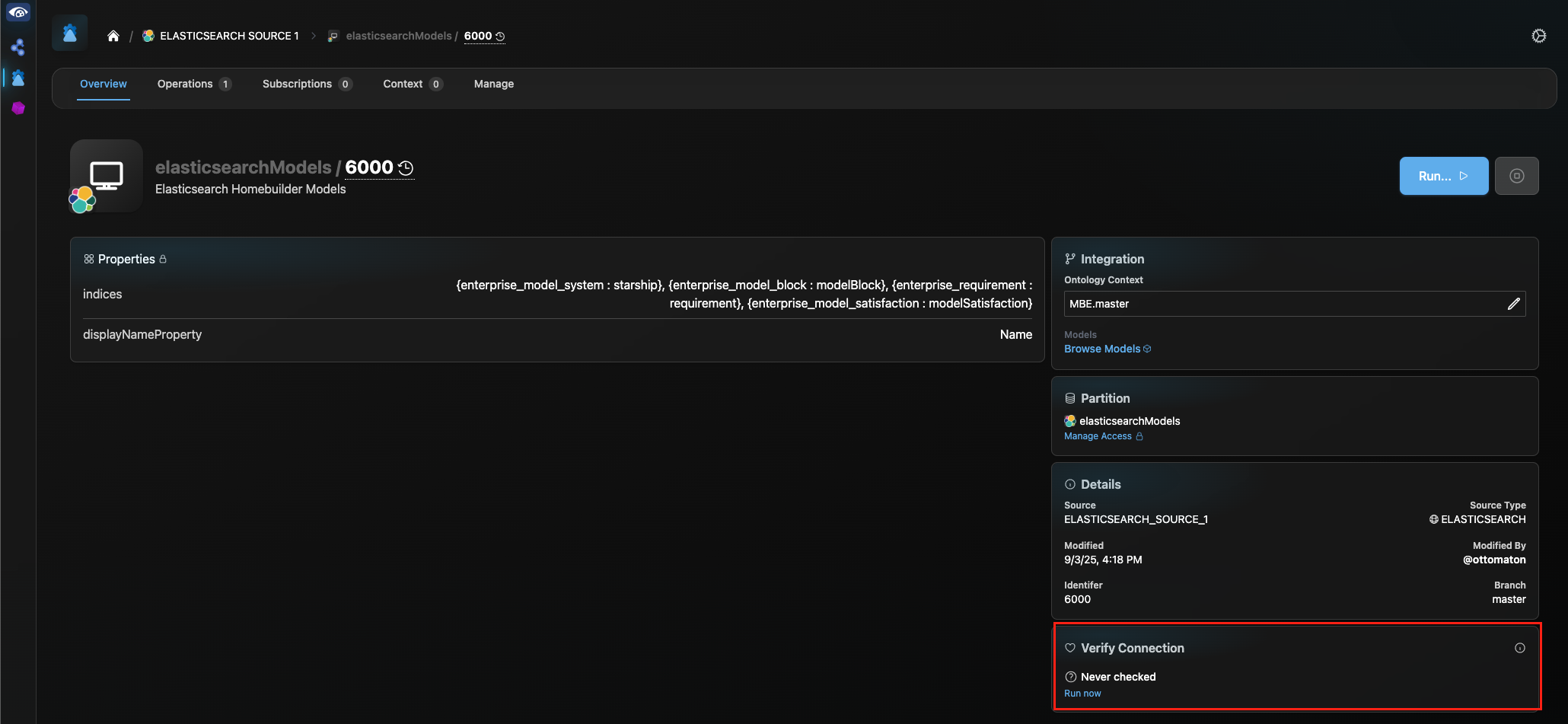
Assuming that Source Type, Source and Channel has been set up, and an initial Publish and/or Refresh have been completed, a Verify operation can be utilized to ensure that records in Elasticsearch are in sync with their representations in the Digital Thread.
On the Overview page of your channel, find the “Verify Connection” pane, and select “Run now”. Enter your Elasticsearch credentials in the pop-up and click “Next”.
Once the pop-up closes, click on “Operations” in the header bar to monitor the progress of the Verify operation. Upon completion, click on the drop down to the right of the Verify progress track and select “Download Logs (Detailed)” to view an item-by-item comparison of each corresponding ES doc/Digital Thread model pair, indicating any discrepancies between the two in properties, relations or metadata.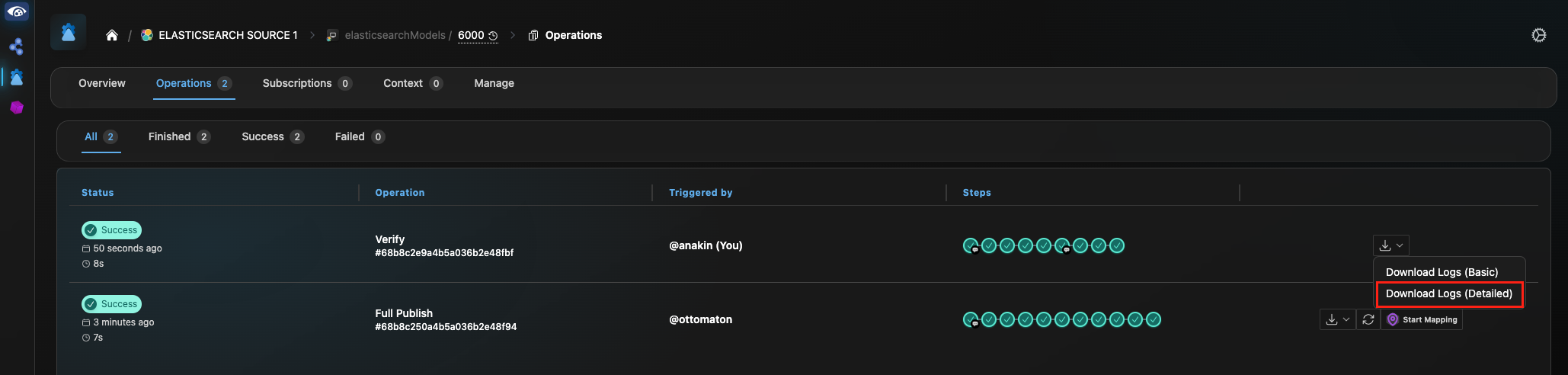
1.7 Advanced Operations
Soft-Refresh
The Soft-Refresh operation is a variation of the Hard Refresh, as described in Section 1.1. A Soft-Refresh is initiated by the “Soft Refresh” button on the “Run” pop-up in the Channel Overview page.
Reset
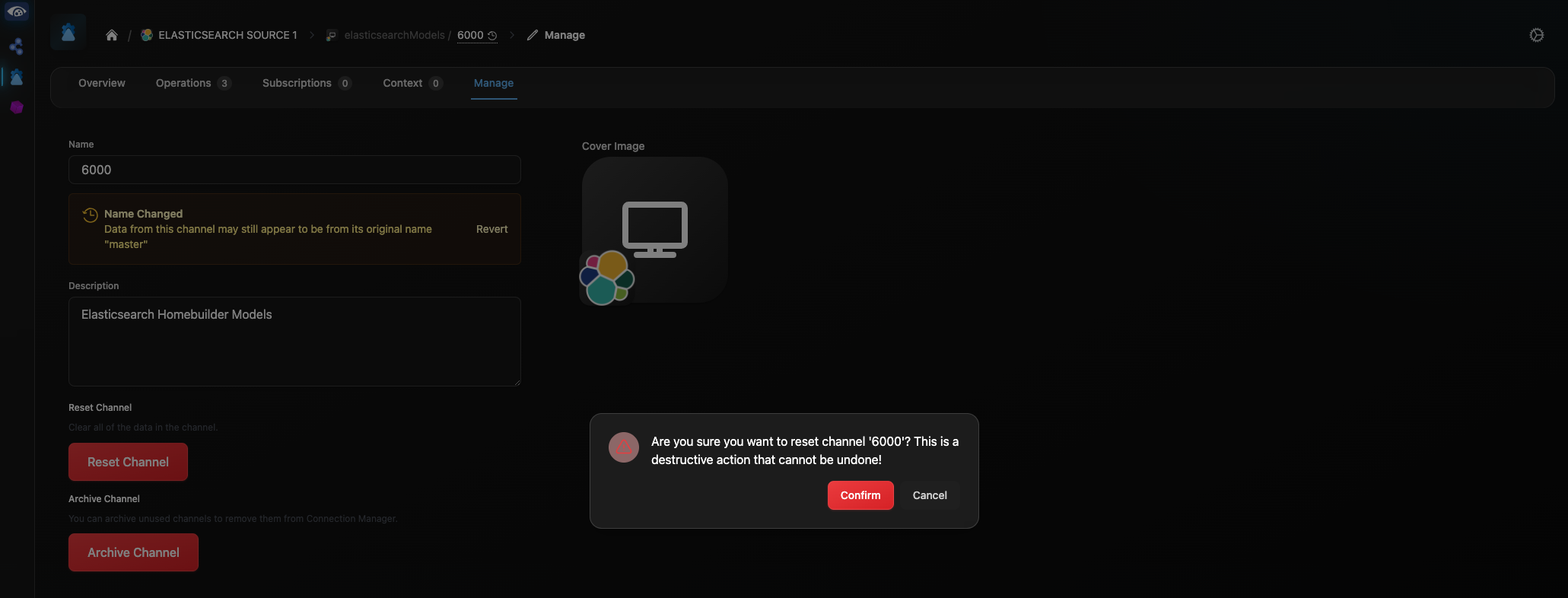
The Reset operation clears all subscription data on the channel. Therefore, running a Reset will remove all subscribed and refreshed data from the connected Elasticsearch project.
Reset is initiated from the Manage tab of the channel. Click “Reset Channel”. In the pop-up, click “Confirm”.
2. Document Overview
2.1 Document Overview
This document provides essential information for using, configuring, and supporting the SBE Vision adapters for Elasticsearch. It covers multiple adapter products, each supporting different versions of the external tool. There is a different version of this document for each major release of the SBE Platform.
2.2 Document Orientation
This document is designed to inform users with various roles:
End Users should begin with Section 1 to understand how to access and operate the adapter, and Section 5 for issues pertaining to the setup, configuration, and use of the digital tool itself.
Digital Thread Specialists should focus on Section 1, and also consult Sections 3, 4, and 5 for deployment and semantic mapping. Section 11 contains details related to mapping items from this tool into a semantic ontology.
Administrators should refer to Section 6 and beyond for setup, security, support, and version management.
3. Adapter Use Cases
3.1 Adapter Overview
The Elasticsearch Adapter is a server-based SBE adapter, allowing the transfer of data from an Elasticsearch NoSQL database to the SBE platform and vis-versa.
Elasticsearch is a distributed search and analytics engine designed to provide near real-time search and analytics for all types of data. Regardless of its search and analytic capabilities, for our purposes, at its heart, Elasticsearch is a NoSQL database that stores object data as JSON formatted documents that can be accessed in bulk or by query.
An Elasticsearch index, simply put, is a collection of documents. Each document in an index may have the same properties (key-value pairs), or they may vary from item to item. However, all fields and their datatypes will be added to the index and available in the schema.
Elasticsearch primarily communicates via the HTTP protocol and is therefore designed to be interacted with via any web-connected system. However, the SBE Elasticsearch adapter utilizes the Elasticsearch Java API, which allows easy access to and interaction with Elasticsearch data via Java-based applications 3.2 Typical Use Cases
Lead By: Solutions
Why this adapter exists
What problem it solves in the system development lifecycle
reqs ↔ architecture with diff/merge in between
Example: “Sync requirements from Tool A to Tool B”
Step-by-step walkthroughs or diagrams
4. Supported Versions
4.1 Supported Adapter Products
7.x
7.0, 7.1, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6, 7.7, 7.9, 7.10, 7.11, 7.12, 7.13
8.x
8.0, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6, 8.7, 8.8, 8.9
4.2 External Tool Versions Supported
All versions of the Elasticsearch Adapter utilize the Elasticsearch Java API 7.16.0. Elasticsearch guarantees forward compatibility, meaning that the adapter will work with any Elasticsearch Server version 7.16 or greater.
4.3 Differences Across Tool Versions
Version 7.0 supported only Publish and Refresh of authoritative data. Support for subscriptions was added in v. 7.1.
Support for relationships in subscription data was added in v. 7.3. The Soft-Refresh operation is supported from v. 7.4 on, and Verify was added in v. 7.5. Version 8.0 is the Melrose equivalent of Woburn v 7.5.
The “indices” channel property was introduced in v. 7.11/8.3 to allow for user defined index-shapeId mappings. In v. 7.0-7.10/8.0-8.2, the Channel Property, “index”, took a list of indices to publish. Subscription refresh would always create/write to indices with the same name as each item’s shapeId. This version also introduced support for refresh of multi-shape subscription items. Version 7.12/8.3 is allows a blank “indices” Channel Property, essentially making the adapter subscription-only.
Finally, v. 7.13/8.4 is the first to support relations in authoritative data via manual entry of relations for authoritative items in the Relations Index. Support for the Reset operation (to clear stale subscription data) was also added in v. 7.13/8.5.
4.4 Supported Plug-Ins and Add-Ons
None - This is a standard SBE server adapter, operated via the SBE web UI or REST API.
(Back To Top)
5. Digital Tool Best Practices
5.1 Tool Configuration Considerations
The Elasticsearch adapter requires minimal configuration.
The target Elasticsearch project must be set in the “connectionString” Data Source Property.
The “indices” Channel Property is optional. However, native (authoritative) Elasticsearch data will only be published to the digital thread if it is in an index included in the “indices” list. Leaving the property blank will allow refresh of subscription data into your project and re-publishing that back to SBE, but no native data will be included.
As described in Section 1.3, if a shapeId is not provided for an published index via an index-shapeId pair within the “indices” property, the shape will be assigned a shapeId sharing its name with the index. Similarly, on refresh, subscription data will be put into an index matching the item’s shapeId, unless otherwise specified in the “indices” property.
Whether using default index-shapeId pairings or specifying them via the “indices” property, it is crucial that the correct shapeIds are used in the ontological mappings for item transformation to succeed during data operations.
5.2 Usage Tips & Gotchas
Elasticsearch specifies its own index naming conventions/restrictions (e.g. all lowercase, with no spaces). The elasticsearch-adapter will modify shapeIds and index names as necessary to meet these conventions.
5.3 Tool Limitations and Workarounds
None Identified
6. Installation
6.1 Installation Instructions
The Elasticsearch Adapter is a server-based tool that runs entirely on an existing
6.2 Configuration
6.3 Source Type Definition
Source Type
The Source Type is a generic designator that tells SBE the identity of the external system that a Data Source, Channel or Connection are targeting. The Elasticsearch adapter handles all operations on Channels tied to Elasticsearch, as indicated by an associated Source Type with name “ELASTICSEARCH”.
The ELASTICSEARCH Source Type can be associated with multiple Sources, thus allowing connection to multiple Elasticsearch projects and indices on different channels. To accommodate this, the Source Type specifies two sets of properties, Server Properties and Channel Properties.
See Section 1.3 for step-by-step instructions to create an ELASTICSEARCH Source Type.
Data Source
The Source specifies the specific Elasticsearch project to which the digital thread will connect. This project location (url) is specified by the “connectionString” Server Property, set up on the Source Type above.
See Section 1.3 for step-by-step instructions to create a Source to connect your Elasticsearch project to the Digital Thread.
7. Channels and Mappings
7.1 Channel Definition
The Channel details the two endpoints of data operations between your Elasticsearch project and the digital thread.
An Elasticsearch Channel requires one Channel Property: “indices”.
The “indices” Channel Property is a list of key:value pairs, with each pair specifying an Elasticsearch index and a corresponding SBE shapeId. During a publish operation, the Elasticsearch adapter will search for each of the indices specified in this list, on the project specified in the connectionString Data Source Property and publish all data in each index. If an index does not exist on the project it will be ignored.
Index-shapeId pairs can also be specified for subscription data. If, for example, a project subscribes to a list of external Requirement items of shapeId “requirement”, and the “indices” property includes the entry “{subscribed_requirements : requirement}”, upon a refresh operation, the Elasticsearch adapter will look for an existing index on the project titled “subscribed_requirements”. If found, the subscription Requirement items will be stored in that index. If the index does not exist, it will be created and populated with the subscription data of shapeId “requirement”.
The “indices” Channel Property must be formatted as below:
”{“index1”:“shapeId1”}, {“index2”:“shapeId2},…{“indexn”:”shapeIdn”}”
See Section 1.3 for step-by-step instructions for Channel Creation.
7.2 Approaches to Mapping
Elasticsearch is a distributed search and analytics engine that stores data as serialized JSON documents. As such, almost any kind of data, comprising any number and combination of fields is able to be represented. There are therefore no pre-defined shapes, shapeIds or mappings for the Elasticsearch Adapter.
In creating mappings, the user must be sure to set the shapeIds to match either the values assigned for each index in the “indices” Channel Property, or the index names that the shapeIds will default to if no mappings are included in “indices”.
Additionally, all fields within the “_source” section of the Elasticsearch doc must be mapped as a property of the shape in order to be included in a publish/refresh.
8. Security and Access
8.1 Authentication Methods
See RFC 006 - Authentication & Authorization for the standard on how to authenticate to use SBE and adapter services.
A user must be logged into the SBE platform as a user with appropriate permissions (Read, Write, and/or Manage) for the operation being performed.
Elasticsearch credentials (username/password) will be requested upon initiation of any Elasticsearch data operation in the platform.
8.2 Authorization and Roles
Role-based access models
User-to-role mapping
8.3 Secure Communication
TLS configuration
Firewall or VPN guidelines
8.4 Identity Integration
LDAP, SSO, or identity federation
9. Release Notes
9.1 Version History
7.15
Implements Bulk Indexing to improve performance of Refresh of large datasets
Reports granular finish states for display in Channel Operations tab
Adds support for SBE Power Types and Base64 conversion
Fixes bug that could throw NPE when accessing an existing by empty control index
Update to java SDK version 7.50
7.14
Implement Reset
Fix bug to allow authoritative relations
Update to java SDK version 7.49
7.12
Fixes but with channel props to allow empty "indices" property
7.11
Indices and shapeIds for both authoritative and subscription items now configurable via channel properties
Allow refresh and re-publish of multi-shape models from SBE
Update to java SDK version 7.45
7.10
Fix bug that caused an error if no control index had been created before refreshing
Update to java SDK version 7.44
7.9
Update to java SDK version 7.43
7.7
Update to java SDK version 7.39
7.6
Fix bugs related to Verify operation, specifically with respect to JSON and timestamp properties
Update SDK version and utilize built-in ServicesFactory
7.5
Add support for Verify functionality
Update custom cert injection for SBE Platform 7.12 release
7.4
Add support for Soft-Refresh functionality
Update to java SDK version 7.33
7.3
Add support for maintaining relations in subscription data.
Added additional support for control index management for subscription items.
Fix bug related to refresh of JSON & Timestamp datatypes.
Update java SDK version
7.1
Basic support for Publish/Refresh operations on authoritative and subscription data.
8.9
Fixes but with HTML Power Type handling
Adds redundancy when looking for relations in the Relations Index during Publish operation
Update to java SDK version 8.18
8.8
Implements additional bug fixes for delta refresh operation
Adopts Item v7 for future ASOT linking functionality
Update to java SDK version 8.17
8.7
Implements bug fixes for delta publish and refresh operations
Update to java SDK version 8.15
8.6
Implements Bulk Indexing to improve performance of Refresh of large datasets
Reports granular finish states for display in Channel Operations tab
Adds support for SBE Power Types and Base64 conversion
Update to java SDK version
8.5
Implement Reset
Update to java sdk 8.11
8.4
Add support for relations in authoritative data
Update to java sdk 8.9
8.3
Change "index" channel property to "indices": {index, shapeId} pairs to map SBE shapes to Elasticsearch indices
Allow blank "indices" channel property for subscription only use case
Allow for refresh and re-publish of multi-shape models from/to SBE
Fix bug preventing subscription refresh without first publishing
Fix Verify bug
Update to java sdk 8.8
8.2
Re-tag HELM chart
8.1
Fix bugs related to Verify operation, specifically with respect to JSON and timestamp properties
Update SDK version and utilize built-in ServicesFactory
8.0
First Melrose release
Adds support for Soft-Refresh and Verify operations, on top of existing Publish, Refresh and Subscription support
10. Technical Reference
10.1 Adapter API Endpoints
The Elasticsearch Adapter operates entirely via the Digital Thread Hub. There are no external API endpoints to the adapter. The adapter itself communicates with the Elasticsearch server via the Elasticsearch Java API. Users can also access and manage their Elasticsearch projects via the standard HTTP API or attached dashboards.
10.2 Identity
All items within an elasticsearch project can be uniquely identified by a combination of the index name and elasticsearch ID (“_id” field at the top level of each doc). These two variables are utilized in the Digital Thread as the unique external identifier for all authoritative and subscription items within a connected Elasticsearch project.
10.3 Configuration File Format Reference
No configuration file is required
10.4 Schema Support
Elasticsearch is a distributed search and analytics engine that stores data as serialized JSON documents. As such, almost any kind of data, comprising any number and combination of fields is able to be represented. There are therefore no pre-defined shapes, shapeIds or mappings for the Elasticsearch Adapter.
In creating mappings, the user must be sure to set the shapeIds to match either the values assigned for each index in the “indices” Channel Property, or the index names that the shapeIds will default to if no mappings are included in “indices”.
Additionally, all fields within the “_source” section of the Elasticsearch doc (see generic example below) must be mapped as a property of the shape in order to be included in a publish/refresh.
CODE{ "_index": "sample_index", "_type": "_doc", "_id": "3002", "_score": 1.0, "_source": { "Property 1 Name": "Property 1 Value", "Property 2 Name": "Property 2 Value", "Property 3 Name": "Property 3 Value", "Property 4 Name": "Property 4 Value", "Property 5 Name": "Property 5 Value" } }Relations between items are stored in Elasticsearch in the “sbe_relations_index” (Relations Index). Since version 8.4, the Elasticsearch Adapter has supported relations in both subscription and authoritative data. On a refresh, Relation Index entries are created automatically for each link on refreshed data. Users are also able to create their own Relation Index entries to represent relations on authoritative data. The schema for the Relations Index is shown below, where the elasticsearchId is the “_id” field value of each item and the “relationExternalName” is the mapped external relation name:
CODE{ "_index": "sbe_relation_index", "_type": "_doc", "_id": "rNvN75YBoY5_HCKc1dxk", "_score": 1.0, "_source": { "sourceName": "Source Item Name", "sourceLocator": { "index": "source_index_name", "elasticsearchId": "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx" }, "sourceShape": "starship", "relationExternalName": "Contains", "targetName": "Target Item Name", "targetLocator": { "index": "target_index_name", "elasticsearchId": "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx" }, "targetOwnership": { "owner": "", "topLevelDomain": "", "channel": "", "type": "UNKNOWN", "dataSource": "", "dataSourceType": "ELASTICSEARCH", "status": "UNKNOWN" } } }
10.5 Compliance and Certification
Maturity | Key Verification Parameters |
|---|---|
Level 1 | Design Ready, Review documentation |
Level 2 | Technology Demonstrated for initial scope. |
Level 3 | Test full-publish, full-refresh on authoritative and subscribed entity sets on current release train. Review Architecture. |
Level 4 | Test all actions on current and future release trains. Test mandatory telemetry. Basic tests are automated. Review Architecture and adoption of best practices. |
Level 5 | Tuned for performance. Introspectable. Full test automation. Stable for 6 months. |
Level 6 | Realizes all domains. Automated L3-L5 tests passes. Stable for 6 months. |
Level 7 | Ongoing security and dependency patches. Stable for a year. |
Elasticsearch Adapter is currently rated at Level 4 in the adapter maturity model.
